Signal sequence contributes to the immunogenicity of Pasteurella multocida lipoprotein E
- PMID: 36423524
- PMCID: PMC9681653
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102200
Signal sequence contributes to the immunogenicity of Pasteurella multocida lipoprotein E
Abstract
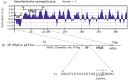
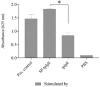
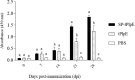
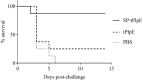
Recombinant Pasterurella multocida lipoprotein E (PlpE) has been shown to protect against fowl cholera. This study aimed to determine if the signal sequence may contribute to the antigenicity and protective efficacy of recombinant PlpE. A small antigenic domain of PlpE (termed truncated PlpE, tPlpE) was constructed with (SP-tPlpE) or without (tPlpE) the signal sequence and evaluated in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, the HEK-Bule hTLR2 Cells were used to evaluate the activation of NF-kB in the test associated with the stimulation of the SP-tPlpE and tPlpE proteins. When chickens were immunized, compared to the tPlpE vaccine group, the SP-tPlpE group showed higher antibody levels and enhanced CD4+ T cell response. In a challenge test, the SP-tPlpE group showed a survival rate of 87.5% (n = 8), compared to 25% for the tPlpE group. It is confirmed that the inclusion of the native signal sequence enhanced protective efficacy against fowl cholera and may act as a vaccine adjuvant. The short SP-tPlpE construct is amenable to further vaccine engineering and has potential to be developed as a fowl cholera vaccine.
Keywords: fowl cholera; lipid moiety; lipoprotein E; signal sequence; subunit vaccine.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Adler B., Bulach D., Chung J., Doughty S., Hunt M., Rajakumar K., Serrano M., van Zanden A., Zhang Y., Ruffolo C. Candidate vaccine antigens and genes in Pasteurella multocida. J. Biotechnol. 1999;73:83–90. - PubMed
-
- Bos M.P., Tommassen J. Biogenesis of the Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2004;7:610–616. - PubMed
-
- Bierer B.W., Derieux W.T. Immunologic response of turkeys to an avirulent Pasteurella multocida vaccine in the drinking water. Poult. Sci. 1972;51:408–416. - PubMed
-
- Braun V., Hantke K. Lipoproteins: structure, function, Biosynthesis. Sub-Cell. Biochem. 2019;92:39–77. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

