Levels of whole salivary advanced glycation end products and interleukin-17 and peri-implant clinical and radiographic status in patients with osteoporosis at 6-years' follow-up
- PMID: 36424586
- PMCID: PMC9685916
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-022-02591-7
Levels of whole salivary advanced glycation end products and interleukin-17 and peri-implant clinical and radiographic status in patients with osteoporosis at 6-years' follow-up
Abstract
Background: There are no studies that have assessed advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and interleukin 17A (IL-17A) levels in whole saliva (WS) of patients with dental implants. The aim was to compare levels of AGEs and IL-17A in WS and peri-implant clinical and radiographic status of patients with and without osteoporosis at 6-years' follow-up.
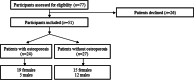
Methods: Osteoporotic (Group-1) and systemically healthy controls (Group-2) having undergone dental implant therapy at least 5 years ago were included. A questionnaire was used to collect information about age, gender, duration and treatment of osteoporosis, number and duration of implants in function, and frequencies of toothbrushing, flossing and hygiene visits. Modified bleeding and plaque indies (mBI and mPI), peri-implant probing depth (PD) and crestal bone loss (CBL) were recorded. WS was collected and levels of AGEs and IL-17A were determined using enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Sample-size estimation was done and statistical analyses were doing using the independent t- and Wilcoxon rank-sum tests. Statistical significance was marked for P-values that were below 0.01.
Results: In patients with (n = 24) and without (n = 27) osteoporosis, implants were in function for 6.3 ± 0.27 and 6.6 ± 0.5 years, respectively. There was no significant difference in peri-implant mBI, PD, mPI and CBL in both groups. Levels of AGE in patients with (119.6 ± 26.5 μg/ml) and without (91.5 ± 14.6 μg/ml) osteoporosis were comparable. Levels of whole salivary IL-17A in patients without and with osteoporosis were 4.6 ± 0.3 and 5.1 ± 0.8 pg/ml, respectively. Flossing of full mouth interproximal spaces once and twice daily toothbrushing daily was reported by 100% patients with osteoporosis. Among patients with osteoporosis 75% and 25% individuals were receiving professional dental prophylaxis every 4 and 6 months, respectively.
Conclusion: Within the limitations of the present study osteoporotic patients are not at an increased risk of peri-implant diseases and can demonstrate salivary AGE and IL-17A levels comparable to non-osteoporotic individuals as long as oral hygiene is stringently maintained.
Keywords: Advanced glycation endproducts; Alveolar bone loss; Osteoporosis; Probing depth.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest and there was no external source of funding for the present study.
Similar articles
-
Periodontal and peri-implant status and whole salivary interleukin 1-beta levels among individuals using selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: an observational study.BMC Oral Health. 2023 May 22;23(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-02908-0. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37217913 Free PMC article.
-
Peri-implant conditions and levels of advanced glycation end products among patients with different glycemic control.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018 Jun;20(3):345-351. doi: 10.1111/cid.12584. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018. PMID: 29350883
-
Peri-Implant Inflammation in Waterpipe Users and Cigarette Smokers: An Observational Study.Int Dent J. 2023 Oct;73(5):717-723. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2023.03.005. Epub 2023 Apr 9. Int Dent J. 2023. PMID: 37037698 Free PMC article.
-
Implant abutment disinfection using plasma of argon and 0.2% and chlorhexidine gel applications immediately before prosthesis delivery: clinical and radiographic status at 5-years of follow-up.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023 Jan;27(1):116-121. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202301_30861. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36647858
-
Peri-implant soft tissue status and crestal bone levels around adjacent implants placed in cigarette smokers and never smokers: Five-year follow-up results.J Periodontol. 2019 Mar;90(3):234-240. doi: 10.1002/JPER.18-0117. Epub 2018 Nov 21. J Periodontol. 2019. PMID: 30311941
References
-
- Gurav AN. Advanced glycation end products: A link between periodontitis and diabetes mellitus? Curr Diabetes Rev. 2013;9(5):355–361. - PubMed
-
- Lalla E, Lamster IB, Stern DM, Schmidt AM. Receptor for advanced glycation end products, inflammation, and accelerated periodontal disease in diabetes: mechanisms and insights into therapeutic modalities. Ann Periodontol. 2001;6(1):113–118. - PubMed
-
- Lalla E, Lamster IB, Schmidt AM. Enhanced interaction of advanced glycation end products with their cellular receptor RAGE: implications for the pathogenesis of accelerated periodontal disease in diabetes. Ann Periodontol. 1998;3(1):13–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous