Reactive Uptake of Gas-Phase NO2 by Urban Road Dust in the Dark
- PMID: 36425340
- PMCID: PMC9677962
- DOI: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.2c00221
Reactive Uptake of Gas-Phase NO2 by Urban Road Dust in the Dark
Abstract
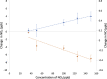
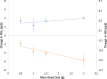
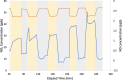
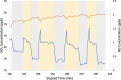
Road dust constitutes a prominent source of anthropogenic particulate matter, making its heterogeneous interactions with common atmospheric gas-phase compounds important. Here, we show that three distinct samples of urban road dust-including dust samples collected from city streets in summer and winter, and an urban park in summer-react with NO2 in the dark, forming NO and surface nitrite. The loss of NO2 ranged from ∼2 to 13% of its gas-phase concentration and scaled with its concentration as well as with the mass of the road dust sample. The uptake of NO2 by the winter dust was ∼4 times greater than that seen from summer street dust, which was in turn greater than that by the park dust. The conversion ratio of NO2 → NO ranged from 0.06 to 0.8 NO produced per NO2 lost and was greatest for the summer park dust. Exposure of the summer road dust to NO2 roughly doubles the concentration of inorganic nitrite anion in the dust but does not produce nitrate. The formation of NO and photolabile nitrite products means that heterogeneous NO x reactions occurring on the surface of road dust in the dark could have wide implications for the oxidative potential of urban areas.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Emerging investigator series: ozone uptake by urban road dust and first evidence for chlorine activation during ozone uptake by agro-based anti-icer: implications for wintertime air quality in high-latitude urban environments.Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2022 Nov 16;24(11):2070-2084. doi: 10.1039/d1em00393c. Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2022. PMID: 36044235
-
[Seasonal variation and function-area difference of PAHs in road dust from Shanghai urban area].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2007 Dec;28(12):2789-93. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2007. PMID: 18290438 Chinese.
-
Land use-related chemical composition of street sediments in Beijing.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2004;11(2):73-83. doi: 10.1007/BF02979706. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2004. PMID: 15108854
-
[Characterization and Formation Mechanism of Water-soluble Inorganic Ions in PM2.5 and PM10 in Summer in the Urban Agglomeration of the Ili River Valley].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2022 Nov 8;43(11):5009-5017. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202201090. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2022. PMID: 36437073 Chinese.
-
Effect of different plant communities on NO2 in an urban road greenbelt in Nanjing, China.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 28;13(1):3424. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30488-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36854721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Environment Canada and Health Canada . Canadian Smog Science Assessment: Highlights and Key Messages, 2012.
-
- Amato F.; Alastuey A.; de la Rosa J.; Gonzalez Castanedo Y.; Sánchez de la Campa A. M.; Pandolfi M.; Lozano A.; Contreras González J.; Querol X. Trends of Road Dust Emissions Contributions on Ambient Air Particulate Levels at Rural, Urban and Industrial Sites in Southern Spain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3533–3544. 10.5194/acp-14-3533-2014. - DOI
-
- Loganathan P.; Vigneswaran S.; Kandasamy J. Road-Deposited Sediment Pollutants: A Critical Review of Their Characteristics, Source Apportionment, and Management. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 1315–1348. 10.1080/10643389.2011.644222. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
