Diagnostic Performance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Detection of Acute Appendicitis in Pregnant Women; a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36426165
- PMCID: PMC9676701
- DOI: 10.22037/aaem.v10i1.1727
Diagnostic Performance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Detection of Acute Appendicitis in Pregnant Women; a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: The diagnosis of acute appendicitis (AA) in pregnant women is commonly challenging owing to the normal results of laboratory tests, organ displacement, and normal physiological inflammatory alterations. This meta-analysis aimed to investigate the accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in diagnosis of AA in pregnant women.
Methods: Two investigators independently performed a comprehensive systematic literature search of electronic databases including MEDLINE, Cochrane Central, EMBASE, Web of Science, Scopus, and Google Scholar to identify studies that reported accuracy of MRI for diagnosis of AA in pregnant women from inception to April 1, 2022.
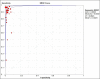
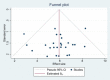
Results: Our systematic search identified a total of 525 published papers. Finally, a total of 26 papers were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivity and specificity of MRI in diagnosis of AA in pregnant women were 0.92 (95% CI: 0.88-0.95) and 0.98 (95% CI 0.97-0.98), respectively. The pooled positive likelihood ratio and negative likelihood ratio were 29.52 (95% CI: 21.90-39.81) and 0.10 (95% CI: 0.04-0.25), respectively. The area under hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic (HSROC) curve indicated that the accuracy of MRI for diagnosis of AA in pregnant women is 99%.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis showed that MRI has high sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for diagnosis of AA in pregnant women and can be used as a first-line imaging modality for suspected cases of AA during pregnancy. Furthermore, it should be noted that when the result of ultrasonography is inconclusive, the use of MRI can reduce unnecessary appendectomy in pregnant patients.
Keywords: Appendicitis; magnetic resonance imaging; meta-analysis; pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Maimaiti A, Aierkin A, Mahmood KM, Apaer S, Maimaiti Y, Yibulayin X, et al. Laparoscopic Appendectomy in Pregnancy With Acute Appendicitis: Single Center Experience With World Review. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2017;27(6):460–4. - PubMed
-
- Franca Neto AH, Amorim MM, Nóbrega BM. Acute appendicitis in pregnancy: literature review. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2015;61(2):170–7. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein MS, Feuerwerker S, Baxter JK. Appendicitis and Cholecystitis in Pregnancy. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2020;63(2):405–15. - PubMed
-
- Moghadam MN, Salarzaei M, Shahraki Z. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound in diagnosing acute appendicitis in pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Emerg Radiol. 2022 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
