The Burden of Urinary Incontinence on Caregivers and Evaluation of Its Impact on Their Emotional Status
- PMID: 36426208
- PMCID: PMC9590664
- DOI: 10.5455/apd.119660
The Burden of Urinary Incontinence on Caregivers and Evaluation of Its Impact on Their Emotional Status
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate caregivers of children with urinary incontinence in terms of the caregiving burden and its associated manifestations.
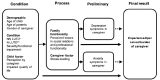
Methods: Caregivers of children who are being treated for urinary incontinence secondary to neurogenic and non-neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTD) were evaluated for caregiver burden (Zarit score), depression (Beck Depression Inventory [BDI]), and anxiety (Beck Anxiety Inventory [BAI]). Additionally, children were evaluated for dysfunctional voiding score. All scores were statistically analyzed for correlation with and relation to the caregiver's emotional status.
Results: Zarit score was equal in caregivers of children with neurogenic and non-neurogenic LUTD. BDI score was higher in caregivers of patients with neurogenic LUTD, whereas BAI score was higher in caregivers of patients with non-neurogenic LUTD. In the evaluation performed, considering the etiological difference, Zarit score in the group with non-neurogenic LUTD correlated positively with BAI and BDI scores. In the neurogenic bladder group, Zarit score correlated with BDI score.
Conclusion: It is important not only in psychiatric patients, but also in those with other chronic disease processes, to evaluate the mental status of caregivers and to support them in dealing with the problem.
Keywords: Caregiver burden; anxiety; depression; urinary incontinence.
© Copyright 2021 authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depression, anxiety and quality of life impairment in parents of children with functional lower urinary tract dysfunction.J Pediatr Urol. 2020 Dec;16(6):838.e1-838.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2020.09.014. Epub 2020 Sep 16. J Pediatr Urol. 2020. PMID: 33012646
-
Evaluation of Anxiety, Depression and Burden on Caregivers of Children with Cerebral Palsy.Dev Neurorehabil. 2021 Nov;24(8):555-560. doi: 10.1080/17518423.2021.1917718. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Dev Neurorehabil. 2021. PMID: 33896338
-
Factors Affecting Psychological Burden on the Informal Caregiver of Patients With Cirrhosis: Looking Beyond the Patient.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2020 Jan-Feb;10(1):9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jun 19. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32025162 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Considerations for Non-Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Children.Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2016 May;8(2):75-85. doi: 10.1111/luts.12123. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2016. PMID: 27111618 Review.
-
[Caregiver burden in relatives of persons with schizophrenia: an overview of measure instruments].Encephale. 2003 Mar-Apr;29(2):137-47. Encephale. 2003. PMID: 14567165 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Caregiver insights on challenges and needs in fecal incontinence products: a mixed methods study.Front Public Health. 2025 Jun 9;13:1453244. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1453244. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40552222 Free PMC article.
-
Association between early and current gastro-intestinal symptoms and co-morbidities in children and adolescents with Angelman syndrome.J Intellect Disabil Res. 2022 Nov;66(11):865-879. doi: 10.1111/jir.12975. Epub 2022 Sep 2. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2022. PMID: 36052644 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources