CX3CR1 deficiency exacerbates immune-mediated hepatitis by increasing NF-κB-mediated cytokine production in macrophage and T cell
- PMID: 36426712
- PMCID: PMC10041049
- DOI: 10.1177/15353702221128573
CX3CR1 deficiency exacerbates immune-mediated hepatitis by increasing NF-κB-mediated cytokine production in macrophage and T cell
Abstract
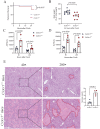
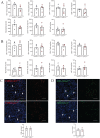
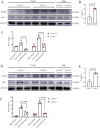
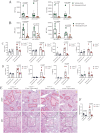
Immune-mediated hepatitis is marked by liver inflammation characterized by immune cell infiltration, chemokine/cytokine production, and hepatocyte injury. C-X3C motif receptor 1 (CX3CR1), as the receptor of chemokine C-X3C motif ligand 1 (CX3CL1)/fractalkine, is mainly expressed on immune cells including monocytes and T cells. Previous studies have shown that CX3CR1 protects against liver fibrosis, but the exact role of CX3CL1/CX3CR1 in acute immune-mediated hepatitis remains unknown. Here, we investigate the role of the CX3CL1/CX3CR1 axis in immune-mediated hepatitis using concanavalin A (ConA)-induced liver injury model in CX3CR1-deficient (Cx3cr1-/-) mice. We observed that Cx3cr1-/- mice had severe liver injury and increased pro-inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-alpha [TNF-α], interferon-gamma [IFN-γ], interleukin-1 beta [IL-1β], and IL-6) in serum and liver compared to wild-type (Cx3cr1+/+) mice after ConA injection. The deficiency of CX3CR1 did not affect ConA-induced immune cell infiltration in liver but led to elevated production of TNF-α in macrophages as well as IFN-γ in T cells after ConA treatment. On the contrary, exogenous CX3CL1 attenuated ConA-induced cytokine production in wild type, but not CX3CR1-deficient macrophages and T cells. Furthermore, in vitro results showed that CX3CR1 deficiency promoted the pro-inflammatory cytokine expression by increasing the phosphorylation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) p65 (p-NF-κB p65). Finally, pre-treatment of p-NF-κB p65 inhibitor, resveratrol, attenuated ConA-induced liver injury and inflammatory responses, especially in Cx3cr1-/- mice. In conclusion, our data show that the deficiency of CX3CR1 promotes pro-inflammatory cytokine production in macrophages and T cells by enhancing the phosphorylation of NF-κB p65, which exacerbates liver injury in ConA-induced hepatitis.
Keywords: CX3CR1; NF-κB p65; T cell; immune-mediated hepatitis; macrophage.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protectin D1 reduces concanavalin A-induced liver injury by inhibiting NF-κB-mediated CX3CL1/CX3CR1 axis and NLR family, pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome activation.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Apr;13(4):3627-38. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.4980. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 26955849
-
Fractalkine (CX3CL1) stimulated by nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)-dependent inflammatory signals induces aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation through an autocrine pathway.Biochem J. 2003 Jul 15;373(Pt 2):547-58. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030207. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12729461 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB-mediated inverse regulation of fractalkine and CX3CR1 during CLP-induced sepsis.Cytokine. 2013 Jan;61(1):97-103. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.08.034. Epub 2012 Sep 29. Cytokine. 2013. PMID: 23026294
-
CX3CL1-CX3CR1 interaction prevents carbon tetrachloride-induced liver inflammation and fibrosis in mice.Hepatology. 2010 Oct;52(4):1390-400. doi: 10.1002/hep.23795. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20683935 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages and the Recovery from Acute and Chronic Inflammation.Annu Rev Physiol. 2017 Feb 10;79:567-592. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034348. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Annu Rev Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27959619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing Liver Delivery of Gold Nanoclusters via Human Serum Albumin Encapsulation for Autoimmune Hepatitis Alleviation.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jan 14;16(1):110. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010110. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38258120 Free PMC article.
-
CX3CL1 (Fractalkine)-CX3CR1 Axis in Inflammation-Induced Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 25;25(9):4679. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094679. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical Study in Mouse Thymus and Thymocytes: Effects of Treatment with a Combination of Sodium Dichloroacetate and Sodium Valproate on Infectious Inflammation Pathways.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Nov 30;15(12):2715. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122715. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38140056 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Common Fractalkine Receptor Variants with Chronic Hepatitis B Patients in Tunisia.Viruses. 2025 Jul 10;17(7):968. doi: 10.3390/v17070968. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40733585 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid-derived growth factor promotes M2 macrophage polarization and attenuates Sjögren's syndrome via suppression of the CX3CL1/CX3CR1 axis.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 21;15:1465938. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1465938. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39497829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chu H, Wang J, Wang Q, Chen J, Li J, Li H, Zhang L. Protective effect of n-butanol extract from Viola yedoensis on immunological liver injury. Chem Biodivers 2021;18:e2001043 - PubMed
-
- Heymann F, Tacke F. Immunology in the liver–from homeostasis to disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;13:88–110 - PubMed
-
- Staumont-Sallé D, Fleury S, Lazzari A, Molendi-Coste O, Hornez N, Lavogiez C, Kanda A, Wartelle J, Fries A, Pennino D, Mionnet C, Prawitt J, Bouchaert E, Delaporte E, Glaichenhaus N, Staels B, Julia V, Dombrowicz D. CX-CL1 (fractalkine) and its receptor CX-CR1 regulate atopic dermatitis by controlling effector T cell retention in inflamed skin. J Exp Med 2014;211:1185–96 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murphy G, Caplice N, Molloy M. Fractalkine in rheumatoid arthritis: a review to date. Rheumatology 2008;47:1446–51 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

