Early risk assessment in paediatric and adult household contacts of confirmed tuberculosis cases by novel diagnostic tests (ERASE-TB): protocol for a prospective, non-interventional, longitudinal, multicountry cohort study
- PMID: 36427173
- PMCID: PMC9301805
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-060985
Early risk assessment in paediatric and adult household contacts of confirmed tuberculosis cases by novel diagnostic tests (ERASE-TB): protocol for a prospective, non-interventional, longitudinal, multicountry cohort study
Abstract
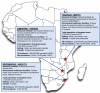
Introduction: The WHO End-TB Strategy calls for the development of novel diagnostics to detect tuberculosis (TB) earlier and more accurately. Better diagnostics, together with tools to predict disease progression, are critical for achieving WHO End-TB targets. The Early Risk Assessment in TB Contacts by new diagnoStic tEsts (ERASE-TB) study aims to evaluate novel diagnostics and testing algorithms for early TB diagnosis and accurate prediction of disease progression among household contacts (HHCs) exposed to confirmed index cases in Mozambique, Tanzania and Zimbabwe.
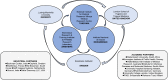
Methods and analysis: A total of 2100 HHCs (aged ≥10 years) of adults with microbiologically-confirmed pulmonary TB will be recruited and followed up at 6-month intervals for 18-24 months. At each time point, a WHO symptom screen and digital chest radiograph (dCXR) will be performed, and blood and urine samples will be collected. Individuals screening positive (WHO symptom screen or dCXR) will be requested to provide sputum for Xpert MTB/Rif Ultra. At baseline, HHCs will also be screened for HIV, diabetes (HbA1c), chronic lung disease (spirometry), hypertension and anaemia. Study outcomes will be coprevalent TB (diagnosed at enrolment), incident TB (diagnosed during follow-up) or no TB at completion of follow-up. Novel diagnostics will be validated using fresh and biobanked samples with a nested case-control design. Cases are defined as HHCs diagnosed with TB (for early diagnosis) or with incident TB (for prediction of progression) and will be matched by age, sex and country to HHCs who remain healthy (controls). Statistical analyses will include assessment of diagnostic accuracy by constructing receiver operating curves and calculation of sensitivity and specificity.
Ethics and dissemination: ERASE-TB has been approved by regulatory and ethical committees in each African country and by each partner organisation. Consent, with additional assent for participants <18 years, is voluntary. Attestation by impartial witnesses is sought in case of illiteracy. Confidentiality of participants is being maintained throughout. Study findings will be presented at scientific conferences and published in peer-reviewed international journals.
Trial registration number: NCT04781257.Cite Now.
Keywords: Diagnostic microbiology; RESPIRATORY MEDICINE (see Thoracic Medicine); Tuberculosis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Global tuberculosis report, 2021. Available: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240037021 [Accessed 28 Oct 2021].
-
- The end TB strategy global strategy and targets for tuberculosis prevention, care and control after 2015 a, 2014. Available: https://www.who.int/tb/strategy/End_TB_Strategy.pdf [Accessed 28 Oct 2021].
-
- WHO . Global tuberculosis report, 2020. Available: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240013131 [Accessed 31 Jul 2021].
-
- TB Disease - Symptoms, treatment & prevention - TBFacts. Available: https://tbfacts.org/tb-disease/ [Accessed 28 Aug 2021].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
