Delayed Formation of Neonatal Reflexes and of Locomotor Skills Is Associated with Poor Maternal Behavior in OXYS Rats Prone to Alzheimer's Disease-like Pathology
- PMID: 36428477
- PMCID: PMC9687320
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10112910
Delayed Formation of Neonatal Reflexes and of Locomotor Skills Is Associated with Poor Maternal Behavior in OXYS Rats Prone to Alzheimer's Disease-like Pathology
Abstract
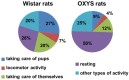
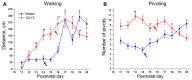
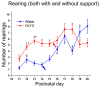
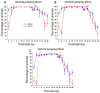
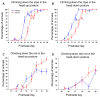
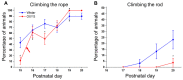
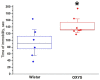
Postnatal brain development is characterized by high plasticity with critical windows of opportunity where any intervention may positively or adversely influence postnatal growth and lead to long-lasting consequences later in life. Poor maternal care is among these interventions. Here, we found that senescence-accelerated OXYS rats prone to an Alzheimer's disease-like pathology are characterized by more passive maternal behavior and insufficient care for pups as compared to control (Wistar) rats. OXYS pups demonstrated a delay in physical development (of auricle detachment, of emergence of pelage and incisors, of eye opening, and of vaginal opening in females) and late manifestation of reflexes and locomotor skills. All observed behavioral abnormalities are connected either with poor coordination of limbs' movements or with a decrease in motivation and development of depression-like behavior. It is possible that their manifestations can be promoted by the features of maternal behavior of OXYS rats. Overall, these early-life events may have long-lasting consequences and contribute to neurodegeneration and development of the Alzheimer's disease-like pathology later in life.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; OXYS rat; early ontogenesis; maternal behavior; motor skill; unconditioned reflex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Postnatal Maturation of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Senescence-Accelerated OXYS Rats, Which Are Prone to an Alzheimer's Disease-like Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 27;24(21):15649. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115649. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958635 Free PMC article.
-
Neurodevelopment and behavior in neonatal OXYS rats with genetically determined accelerated senescence.Brain Res. 2018 Feb 15;1681:75-84. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.12.021. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29274882
-
Alterations of hippocampal neurogenesis during development of Alzheimer's disease-like pathology in OXYS rats.Exp Gerontol. 2019 Jan;115:32-45. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2018.11.008. Epub 2018 Nov 8. Exp Gerontol. 2019. PMID: 30415068
-
Senescence-accelerated OXYS rats: a model of age-related cognitive decline with relevance to abnormalities in Alzheimer disease.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(6):898-909. doi: 10.4161/cc.28255. Epub 2014 Feb 17. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24552807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The senescence-accelerated oxys rats--a genetic model of premature aging and age-dependent degenerative diseases].Adv Gerontol. 2014;27(2):336-40. Adv Gerontol. 2014. PMID: 25306668 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
The Rat Brain Transcriptome: From Infancy to Aging and Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease-like Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 11;24(2):1462. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021462. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674977 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

