Eumelanin from the Black Soldier Fly as Sustainable Biomaterial: Characterisation and Functional Benefits in Tissue-Engineered Composite Scaffolds
- PMID: 36428512
- PMCID: PMC9687302
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10112945
Eumelanin from the Black Soldier Fly as Sustainable Biomaterial: Characterisation and Functional Benefits in Tissue-Engineered Composite Scaffolds
Abstract
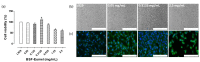
An optimized extraction protocol for eumelanins from black soldier flies (BSF-Eumel) allows an in-depth study of natural eumelanin pigments, which are a valuable tool for the design and fabrication of sustainable scaffolds. Here, water-soluble BSF-Eumel sub-micrometer colloidal particles were used as bioactive signals for developing a composite biomaterial ink for scaffold preparation. For this purpose, BSF-Eumel was characterized both chemically and morphologically; moreover, biological studies were carried out to investigate the dose-dependent cell viability and its influence on human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs), with the aim of validating suitable protocols and to find an optimal working concentration for eumelanin-based scaffold preparation. As proof of concept, 3D printed scaffolds based on methacrylated hyaluronic acid (MEHA) and BSF-Eumel were successfully produced. The scaffolds with and without BSF-Eumel were characterized in terms of their physico-chemical, mechanical and biological behaviours. The results showed that MEHA/BSF-Eumel scaffolds had similar storage modulus values to MEHA scaffolds. In terms of swelling ratio and stability, these scaffolds were able to retain their structure without significant changes over 21 days. Biological investigations demonstrated the ability of the bioactivated scaffolds to support the adhesion, proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells.
Keywords: 3D printing; bone tissue engineering; eumelanins; hyaluronic acid; methacrylated hyaluronic acid; scaffolds.
Conflict of interest statement
Insectta Pte. Ltd. filed a patent application regarding the extraction of melanin from black soldier flies. Jun Wei Phua and Christoph Ottenheim are listed as inventors. Jun Wei Phua holds shares in Insectta Pte. Ltd. The authors declare that there are no other conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Migliaccio L., Manini P., Altamura D., Giannini C., Tassini P., Maglione M.G., Minarini C., Pezzella A. Evidence of Unprecedented High Electronic Conductivity in Mammalian Pigment Based Eumelanin Thin Films After Thermal Annealing in Vacuum. Front. Chem. 2019;7:162. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00162. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

