Tat-hspb1 Suppresses Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC) Growth via Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization
- PMID: 36428802
- PMCID: PMC9688814
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14225710
Tat-hspb1 Suppresses Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC) Growth via Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization
Abstract
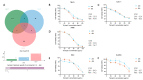
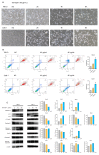
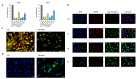
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the most prevalent kidney cancer, of which the incidence is increasing worldwide with a high mortality rate. Bioactive peptides are considered a significant class of natural medicines. We applied mass spectrometry-based peptidomic analysis to explore the peptide profile of human renal clear cell carcinoma and adjacent normal tissues. A total of 18,031 peptides were identified, of which 105 unique peptides were differentially expressed (44 were up-regulated and 61 were down-regulated in ccRCC tissues). Through bioinformatic analysis, we finally selected one peptide derived from the HSPB1 protein (amino acids 12-35 of the N-terminal region of HSPB1). Next, we fused this peptide to the HIV-Tat, generated a novel peptide named Tat-hspb1, and found that Tat-hspb1 inhibited ccRCC cells' viability while being less cytotoxic to normal epithelial cells. Furthermore, Tat-hspb1 induced apoptosis and inhibited the proliferation and migration of ccRCC cells. Furthermore, we demonstrated that Tat-hspb1 was predominantly localized in lysosomes after entering the ccRCC cell and induced lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP) and the release of cathepsin D from lysosomes. Taken together, Tat-hspb1 has the potential to serve as a new anticancer drug candidate.
Keywords: apoptosis; lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP); peptide; renal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Shuch B., Amin A., Armstrong A.J., Eble J.N., Ficarra V., Lopez-Beltran A., Martignoni G., Rini B.I., Kutikov A. Understanding pathologic variants of renal cell carcinoma: Distilling therapeutic opportunities from biologic complexity. Eur. Urol. 2015;67:85–97. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.04.029. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

