The Complex Journey of the Calcium Regulation Downstream of TAS2R Activation
- PMID: 36429066
- PMCID: PMC9688576
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11223638
The Complex Journey of the Calcium Regulation Downstream of TAS2R Activation
Abstract
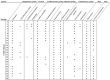
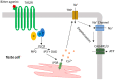
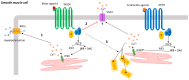
Bitter taste receptors (TAS2Rs) have recently arisen as a potential drug target for asthma due to their localization in airway cells. These receptors are expressed in all cell types of the respiratory system comprising epithelial, smooth muscle and immune cells; however, the expression pattern of the subtypes is different in each cell type and, accordingly, so is their role, for example, anti-inflammatory or bronchodilator. The most challenging aspect in studying TAS2Rs has been the identification of the downstream signaling cascades. Indeed, TAS2R activation leads to canonical IP3-dependent calcium release from the ER, but, alongside, there are other mechanisms that differ according to the histological localization. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge on the cytosolic calcium modulation downstream of TAS2R activation in the epithelial, smooth muscle and immune cells of the airway system.
Keywords: bitter taste receptors; calcium signaling; epithelial lung cells; respiratory system; smooth muscle cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lush I.E., Hornigold N., King P., Stoye J.P. The genetics of tasting in mice. VII. Glycine revisited, and the chromosom.al location of Sac and Soa. Genet. Res. 1995;66:167–174. doi: 10.1017/S0016672300034510. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

