Contamination, Source Identification, Ecological and Human Health Risks Assessment of Potentially Toxic-Elements in Soils of Typical Rare-Earth Mining Areas
- PMID: 36429823
- PMCID: PMC9690513
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192215105
Contamination, Source Identification, Ecological and Human Health Risks Assessment of Potentially Toxic-Elements in Soils of Typical Rare-Earth Mining Areas
Abstract
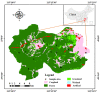
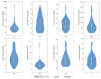
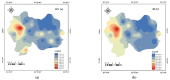
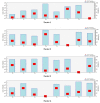
The mining and leaching processes of rare-earth mines can include the entry of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) into the environment, causing ecological risks and endangering human health. However, the identification of ecological risks and sources of PTEs in rare-earth mining areas is less comprehensive. Hence, we determine the PTE (Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, Zn, V) content in soils around rare-earth mining areas in the south and analyze the ecological health risks, distribution characteristics, and sources of PTEs in the study area using various indices and models. The results showed that the average concentrations of Co, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn were higher than the soil background values, with a maximum of 1.62 times. The spatial distribution of PTEs was not homogeneous and the hot spots were mostly located near roads and mining areas. The ecological risk index and the non-carcinogenic index showed that the contribution was mainly from Co, Pb, and Cr, which accounted for more than 90%. Correlation analysis and PMF models indicated that eight PTEs were positively correlated, and rare-earth mining operations (concentration of 22.85%) may have caused Pb and Cu enrichment in soils in the area, while other anthropogenic sources of pollution were industrial emissions and agricultural pollution. The results of the study can provide a scientific basis for environmental-pollution assessment and prevention in rare-earth mining cities.
Keywords: human health risks; mining areas; potentially toxic elements; source allocation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Zhao K., Yang Y., Peng H., Zhang L., Zhou Y., Zhang J., Du C., Liu J., Lin X., Wang N., et al. Silicon fertilizers, humic acid and their impact on physicochemical properties, availability and distribution of heavy metals in soil and soil aggregates. Sci. Total Environ. 2022;822:153483. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153483. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

