Influence of Sedentary Behaviour Interventions on Vascular Functions and Cognitive Functions in Hypertensive Adults-A Scoping Review on Potential Mechanisms and Recommendations
- PMID: 36429835
- PMCID: PMC9690278
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192215120
Influence of Sedentary Behaviour Interventions on Vascular Functions and Cognitive Functions in Hypertensive Adults-A Scoping Review on Potential Mechanisms and Recommendations
Abstract
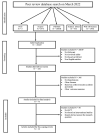
Since the workplace has become desk-based and leisure time has become dominated by digital relaxation modes, the world is moving at a pace where physical activity has become a time-bound routine. The negative effects of extended sitting are a global concern since the workforce is becoming more desk based. There is a dearth of reviews that may link the knowledge on the effects of sedentary behaviour on hypertension and its accompanying damage to the brain and blood vessels and provide a future scope for the investigations connected to the relationship between sedentary behaviour and hypertension. Methods: Based on the database search and extensive research we did, we found studies that concentrated on the adverse effects of sedentary behaviour in association with blood pressure, cognitive decline and brain damage on adults. Results: We extracted 12 articles out of 20,625. We identified the potential adverse effects of sedentary behaviour, methods to reduce sedentary behaviour and the positive changes on health due to the interventions introduced. Sedentary lifestyle has shown a decline in human health. However, the visible symptoms presented later in life makes it very important to know the areas of decline and look for ways to curb the decline or procrastinate it.
Keywords: cerebral prefusion; hypertension; mean arterial pressure; prolonged sitting; pulsed wave velocity; sedentary behaviour; systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
-
- Dachs B. The Impact of New Technologies on the Labour Market and the Social Economy. Volume 148. European Commission; Brussels, Belgium: 2018. [(accessed on 9 October 2022)]. ISBN 9789284625864. Available online: https://www.voced.edu.au/content/ngv:80681.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical