Cell Metabolomics Reveals the Potential Mechanism of Aloe Emodin and Emodin Inhibiting Breast Cancer Metastasis
- PMID: 36430215
- PMCID: PMC9694700
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232213738
Cell Metabolomics Reveals the Potential Mechanism of Aloe Emodin and Emodin Inhibiting Breast Cancer Metastasis
Abstract
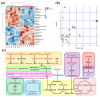
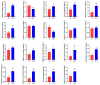
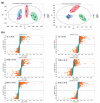
Metastasis is one of the main obstacles for the treatment and prognosis of breast cancer. In this study, the effects and possible mechanisms of aloe emodin (AE) and emodin (EMD) for inhibiting breast cancer metastasis were investigated via cell metabolomics. First, a co-culture model of MCF-7 and HUVEC cells was established and compared with a traditional single culture of MCF-7 cells. The results showed that HUVEC cells could promote the development of cancer cells to a malignant phenotype. Moreover, AE and EMD could inhibit adhesion, invasion, and angiogenesis and induce anoikis of MCF-7 cells in co-culture model. Then, the potential mechanisms behind AE and EMD inhibition of MCF-7 cell metastasis were explored using a metabolomics method based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MS multivariate statistical analysis. Consequently, 27 and 13 biomarkers were identified in AE and EMD groups, respectively, including polyamine metabolism, methionine cycle, TCA cycle, glutathione metabolism, purine metabolism, and aspartate synthesis. The typical metabolites were quantitatively analyzed, and the results showed that the inhibitory effect of AE was significantly better than EMD. All results confirmed that AE and EMD could inhibit metastasis of breast cancer cells through different pathways. Our study provides an overall view of the underlying mechanisms of AE and EMD against breast cancer metastasis.
Keywords: aloe emodin (AE); breast cancer; cell metabolomics; emodin (EMD); metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The effects and mechanisms of aloe-emodin on reversing adriamycin-induced resistance of MCF-7/ADR cells.Phytother Res. 2021 Jul;35(7):3886-3897. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7096. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Phytother Res. 2021. PMID: 33792091
-
LC-MS based urinary metabolomics study of the intervention effect of aloe-emodin on hyperlipidemia rats.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Jul 15;156:104-115. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.04.015. Epub 2018 Apr 16. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29698861
-
Exploring a Novel Target Treatment on Breast Cancer: Aloe-emodin Mediated Photodynamic Therapy Induced Cell Apoptosis and Inhibited Cell Metastasis.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2016;16(6):763-70. doi: 10.2174/1871520615666150821093323. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26295333
-
Potential antineoplastic effects of Aloe-emodin: a comprehensive review.Am J Chin Med. 2014;42(2):275-88. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X14500189. Am J Chin Med. 2014. PMID: 24707862 Review.
-
The isomers, aloe-emodin and emodin, possess differential inhibitory activities against CYP1B1 enzyme.Steroids. 2022 Sep;185:109055. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2022.109055. Epub 2022 Jun 2. Steroids. 2022. PMID: 35661798 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural anti-cancer products: insights from herbal medicine.Chin Med. 2025 Jun 9;20(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01124-y. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40490812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Phytochemicals in Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 26;24(9):7863. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097863. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cao Z., Ding B.S., Guo P., Lee S.B., Butler J.M., Casey S.C., Simons M., Tam W., Felsher D.W., Shido K., et al. Angiocrine factors deployed by tumor vascular niche induce B cell lymphoma invasiveness and chemoresistance. Cancer Cell. 2014;25:350–365. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.02.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

