Insights into Antiviral Properties and Molecular Mechanisms of Non-Flavonoid Polyphenols against Human Herpesviruses
- PMID: 36430369
- PMCID: PMC9693824
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232213891
Insights into Antiviral Properties and Molecular Mechanisms of Non-Flavonoid Polyphenols against Human Herpesviruses
Abstract
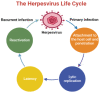
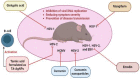
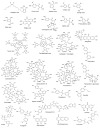
Herpesviruses are one of the most contagious DNA viruses that threaten human health, causing severe diseases, including, but not limited to, certain types of cancer and neurological complications. The overuse and misuse of anti-herpesvirus drugs are key factors leading to drug resistance. Therefore, targeting human herpesviruses with natural products is an attractive form of therapy, as it might improve treatment efficacy in therapy-resistant herpesviruses. Plant polyphenols are major players in the health arena as they possess diverse bioactivities. Hence, in this article, we comprehensively summarize the recent advances that have been attained in employing plant non-flavonoid polyphenols, such as phenolic acids, tannins and their derivatives, stilbenes and their derivatives, lignans, neolignans, xanthones, anthraquinones and their derivatives, curcuminoids, coumarins, furanocoumarins, and other polyphenols (phloroglucinol) as promising anti-herpesvirus drugs against various types of herpesvirus such as alpha-herpesviruses (herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 and varicella-zoster virus), beta-herpesviruses (human cytomegalovirus), and gamma-herpesviruses (Epstein-Barr virus and Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus). The molecular mechanisms of non-flavonoid polyphenols against the reviewed herpesviruses are also documented.
Keywords: Epstein–Barr virus (EBV); HSV-1; HSV-2; Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV); antiviral activity; herpes simplex virus; human cytomegalovirus (HCMV); natural products; non-flavonoid polyphenols; polyphenols; varicella-zoster virus (VZV).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Flavonoids Target Human Herpesviruses That Infect the Nervous System: Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Insights.Viruses. 2022 Mar 13;14(3):592. doi: 10.3390/v14030592. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35336999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Prevention and therapy of herpesvirus infections].Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1985 Feb;180(2-3):107-20. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1985. PMID: 2986378 Review. German.
-
A single tube PCR assay for simultaneous amplification of HSV-1/-2, VZV, CMV, HHV-6A/-6B, and EBV DNAs in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with virus-related neurological diseases.J Neurovirol. 2000 Oct;6(5):410-7. doi: 10.3109/13550280009018305. J Neurovirol. 2000. PMID: 11031694
-
Animal models of human herpesvirus infection.Animal Model Exp Med. 2025 Apr;8(4):615-628. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12575. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Animal Model Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 39921263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of carbohydrate-related metabolism in Herpesvirus infections.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2023 May 17;4:100192. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2023.100192. eCollection 2023. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2023. PMID: 37273578 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 Complications: Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Mitochondrial and Endothelial Dysfunction.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 4;24(19):14876. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914876. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic Perspectives on Herpes Simplex Virus Inhibition by Phenolic Acids and Tannins: Interference with the Herpesvirus Life Cycle.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 20;26(13):5932. doi: 10.3390/ijms26135932. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Quest for Immunity: Exploring Human Herpesviruses as Vaccine Vectors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 9;24(22):16112. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216112. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Epstein-Barr Virus Activities of Flavones and Flavonols with Effects on Virus-Related Cancers.Molecules. 2025 Feb 26;30(5):1058. doi: 10.3390/molecules30051058. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40076282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Antiviral Activity of Kalanchoe daigremontiana Extract against Human Herpesvirus Type 1.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7507. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147507. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062750 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

