2cChIP-seq and 2cMeDIP-seq: The Carrier-Assisted Methods for Epigenomic Profiling of Small Cell Numbers or Single Cells
- PMID: 36430462
- PMCID: PMC9692998
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232213984
2cChIP-seq and 2cMeDIP-seq: The Carrier-Assisted Methods for Epigenomic Profiling of Small Cell Numbers or Single Cells
Abstract
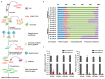
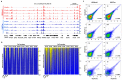
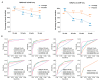
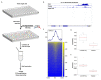
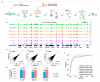
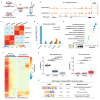
Chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with high-throughput sequencing (ChIP-seq) can profile genome-wide epigenetic marks associated with regulatory genomic elements. However, conventional ChIP-seq is challenging when examining limited numbers of cells. Here, we developed a new technique by supplementing carrier materials of both chemically modified mimics with epigenetic marks and dUTP-containing DNA fragments during conventional ChIP procedures (hereafter referred to as 2cChIP-seq), thus dramatically improving immunoprecipitation efficiency and reducing DNA loss of low-input ChIP-seq samples. Using this strategy, we generated high-quality epigenomic profiles of histone modifications or DNA methylation in 10-1000 cells. By introducing Tn5 transposase-assisted fragmentation, 2cChIP-seq reliably captured genomic regions with histone modification at the single-cell level in about 100 cells. Moreover, we characterized the methylome of 100 differentiated female germline stem cells (FGSCs) and observed a particular DNA methylation signature potentially involved in the differentiation of mouse germline stem cells. Hence, we provided a reliable and robust epigenomic profiling approach for small cell numbers and single cells.
Keywords: female germline stem cells; low-input ChIP-seq; low-input MeDIP-seq; single-cell ChIP-seq.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A chromatin integration labelling method enables epigenomic profiling with lower input.Nat Cell Biol. 2019 Feb;21(2):287-296. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0248-3. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Nat Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30532068
-
Genome-wide epigenomic profiling for biomarker discovery.Clin Epigenetics. 2016 Nov 21;8:122. doi: 10.1186/s13148-016-0284-4. eCollection 2016. Clin Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 27895806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Profiling the Epigenetic Landscape of the Spermatogonial Stem Cell-Part 1: Epigenomics Assays.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2656:71-108. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3139-3_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37249867
-
Profiling the Epigenetic Landscape of the Spermatogonial Stem Cell: Part 2-Computational Analysis of Epigenomics Data.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2656:109-125. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3139-3_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37249868
-
Role of ChIP-seq in the discovery of transcription factor binding sites, differential gene regulation mechanism, epigenetic marks and beyond.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(18):2847-52. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.949201. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486472 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rewriting cellular fate: epigenetic interventions in obesity and cellular programming.Mol Med. 2024 Oct 10;30(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00944-2. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39390356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-Cell DNA Methylation Analysis in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;14(24):6171. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246171. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551655 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

