Polyphosphate Activates von Willebrand Factor Interaction with Glycoprotein Ib in the Absence of Factor VIII In Vitro
- PMID: 36430595
- PMCID: PMC9692336
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232214118
Polyphosphate Activates von Willebrand Factor Interaction with Glycoprotein Ib in the Absence of Factor VIII In Vitro
Abstract
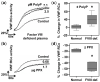
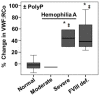
Polyphosphate (polyP), a phosphate polymer released by activated platelets, may modulate various stages of hemostasis by binding to blood proteins. In this context, we previously reported that polyP binds to the von Willebrand factor (VWF). One of the most significant functions of VWF is to bind to and protect the blood circulating Factor VIII (FVIII). Therefore, here, we study the role of polyP in the VWF-FVIII complex in vitro and suggest its biological significance. Surface plasmon resonance and electrophoretic mobility assays indicated that polyP binds dynamically to VWF only in the absence of FVIII. Using the VWF Ristocetin Cofactor assay, the most accepted method for studying VWF in platelet adhesion, we found that polyP activates this role of VWF only at low levels of FVIII, such as in plasmas with chemically depleted FVIII and plasmas from severe hemophilia A patients. Moreover, we demonstrated that FVIII competes with polyP in the activation of VWF. Finally, polyP also increases the binding of VWF to platelets in samples from patients with type 2 and type 3 von Willebrand disease. We propose that polyP may be used in designing new therapies to activate VWF when FVIII cannot be used.
Keywords: factor VIII; hemophilia A; polyphosphates; von Willebrand diseases; von Willebrand factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

