High Instantaneous Inhibitory Potential of Bictegravir and the New Spiro-β-Lactam BSS-730A for HIV-2 Isolates from RAL-Naïve and RAL-Failing Patients
- PMID: 36430777
- PMCID: PMC9695772
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232214300
High Instantaneous Inhibitory Potential of Bictegravir and the New Spiro-β-Lactam BSS-730A for HIV-2 Isolates from RAL-Naïve and RAL-Failing Patients
Abstract
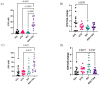
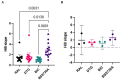
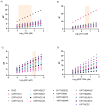
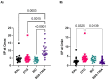
Integrase inhibitors (INIs) are an important class of drugs for treating HIV-2 infection, given the limited number of drugs active against this virus. While the clinical efficacy of raltegravir and dolutegravir is well established, the clinical efficacy of bictegravir for treating HIV-2 infected patients has not been determined. Little information is available regarding the activity of bictegravir against HIV-2 isolates from patients failing raltegravir-based therapy. In this study, we examined the phenotypic and matched genotypic susceptibility of HIV-2 primary isolates from raltegravir-naïve and raltegravir-failing patients to raltegravir, dolutegravir, and bictegravir, and to the new spiro-β-lactam BSS-730A. The instantaneous inhibitory potential (IIP) was calculated to help predict the clinical activity of bictegravir and BSS-730A. Isolates from raltegravir-naïve patients were highly sensitive to all INIs and BSS-730A. Combined integrase mutations E92A and Q148K conferred high-level resistance to raltegravir, and E92Q and T97A conferred resistance to raltegravir and dolutegravir. The antiviral activity of bictegravir and BSS-730A was not affected by these mutations. BSS-730A displayed strong antiviral synergism with raltegravir. Mean IIP values at Cmax were similar for all INIs and were not significantly affected by resistance mutations. IIP values were significantly higher for BSS-730A than for INIs. The high IIP values of bictegravir and BSS-730A for raltegravir-naïve and raltegravir-resistant HIV-2 isolates highlight their potential value for treating HIV-2 infection. Overall, the results are consistent with the high clinical efficacy of raltegravir and dolutegravir for HIV-2 infection and suggest a promising clinical profile for bictegravir and BSS-730A.
Keywords: HIV-2; antiretroviral activity; drug resistance; instantaneous inhibitory potential (IIP); integrase inhibitors (INIs); spiro-β-lactam BSS-730A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Faria N.R., Hodges-Mameletzis I., Silva J.C., Rodes B., Erasmus S., Paolucci S., Ruelle J., Pieniazek D., Taveira N., Trevino A., et al. Phylogeographical footprint of colonial history in the global dispersal of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 group A. Pt 4J. Gen. Virol. 2012;93:889–899. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.038638-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Faria N.R. Phylogeographic Insights into the Origins and Epidemic History of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 2. In: Hope T.J., Richman D., Stevenson M., editors. Encyclopedia of AIDS. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2013.
-
- Direção-Geral da Saúde, Instituto Nacional de Saúde Doutor Ricardo Jorge . Infeção VIH e SIDA em Portugal—2020. Direção-Geral da Saúde, Instituto Nacional de Saúde Doutor Ricardo Jorge; Lisboa, Portugal: 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

