Functional Insights into Protein Kinase A (PKA) Signaling from C. elegans
- PMID: 36431013
- PMCID: PMC9692727
- DOI: 10.3390/life12111878
Functional Insights into Protein Kinase A (PKA) Signaling from C. elegans
Abstract
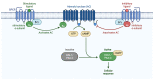
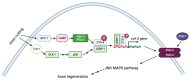
Protein kinase A (PKA), which regulates a diverse set of biological functions downstream of cyclic AMP (cAMP), is a tetramer consisting of two catalytic subunits (PKA-C) and two regulatory subunits (PKA-R). When cAMP binds the PKA-R subunits, the PKA-C subunits are released and interact with downstream effectors. In Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), PKA-C and PKA-R are encoded by kin-1 and kin-2, respectively. This review focuses on the contributions of work in C. elegans to our understanding of the many roles of PKA, including contractility and oocyte maturation in the reproductive system, lipid metabolism, physiology, mitochondrial function and lifespan, and a wide variety of behaviors. C. elegans provides a powerful genetic platform for understanding how this kinase can regulate an astounding variety of physiological responses.
Keywords: C. elegans; PKA; behavior; cAMP; calcium signaling; physiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Gα/GSA-1 works upstream of PKA/KIN-1 to regulate calcium signaling and contractility in the Caenorhabditis elegans spermatheca.PLoS Genet. 2020 Aug 10;16(8):e1008644. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008644. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32776941 Free PMC article.
-
PKA/KIN-1 mediates innate immune responses to bacterial pathogens in Caenorhabditis elegans.Innate Immun. 2017 Nov;23(8):656-666. doi: 10.1177/1753425917732822. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Innate Immun. 2017. PMID: 28958206
-
Protein Kinase A Subunit Balance Regulates Lipid Metabolism in Caenorhabditis elegans and Mammalian Adipocytes.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 23;291(39):20315-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.740464. Epub 2016 Aug 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27496951 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase A catalytic subunit isoform PRKACA; History, function and physiology.Gene. 2016 Feb 15;577(2):101-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.11.052. Epub 2015 Dec 12. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26687711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Molecular Basis for Specificity at the Level of the Protein Kinase a Catalytic Subunit.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Sep 12;9:538. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00538. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30258407 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rosmarinic Acid Present in Lepechinia floribunda and Lepechinia meyenii as a Potent Inhibitor of the Adenylyl Cyclase gNC1 from Giardia lamblia.Plants (Basel). 2024 Feb 26;13(5):646. doi: 10.3390/plants13050646. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475493 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide RNAi screening in C. elegans reveals OXPHOS and pyrimidine synthesis pathways as PKA regulators.Commun Biol. 2025 Aug 26;8(1):1280. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08718-0. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40855216 Free PMC article.
-
Redox Regulation of cAMP-Dependent Protein Kinase and Its Role in Health and Disease.Life (Basel). 2025 Apr 16;15(4):655. doi: 10.3390/life15040655. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283209 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

