Effect of Soil Type on Native Pterocypsela laciniata Performance under Single Invasion and Co-Invasion
- PMID: 36431033
- PMCID: PMC9695812
- DOI: 10.3390/life12111898
Effect of Soil Type on Native Pterocypsela laciniata Performance under Single Invasion and Co-Invasion
Abstract
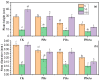
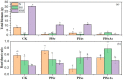
Native and invasive plant competition is usually controlled by the soil properties and the soil type underlying interspecific interactions. However, many uncertainties exist regarding the impact of soil type on native plant growth under single invasion and co-invasion despite the significant number of previous studies that focused on plant invasion. This study aims to elucidate the effects of soil type on the response of the native plant Pterocypsela laciniata under single invasion and co-invasion. Three different soils were used: natural soil, nutrient soil, and nutrient sterilized soil. The native P. laciniata was grown in monoculture and under single invasion and co-invasion with Solidago canadensis and Aster subulatus Michx. The results show that the native plant height and total biomass were 75% and 93.33% higher, respectively, in nutrient sterilized soil in monoculture than in natural and nutrient soil. In contrast, the native P. laciniata presents its best competitive ability in nutrient sterilized soil, being about 100% higher than in natural and nutrient soil under single invasion and co-invasion. However, no significant increase was observed in its growth parameters under co-invasion compared to single invasion. Conclusively, this study shows that nutrient soil sterilization positively affects native plant growth in monoculture and under single invasion, contrasting co-invasion in which more pronounced negative effects were observed on the native plant response.
Keywords: Pterocypsela laciniata; co-invasion; single invasion; soil diversity; soil type.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Symonds J.E. Ph.D. Thesis. University of British Columbia; Vancouver, BC, Canada: 2011. Patterns and Ecological Consequences of Exotic Plant Invasion in Canada’s Endangered Antelope-Brush Ecosystem.
-
- Wavrek M., Heberling J.M., Fei S., Kalisz S. Herbaceous invaders in temperate forests: A systematic review of their ecology and proposed mechanisms of invasion. Biol. Invasions. 2017;19:3079–3097. doi: 10.1007/s10530-017-1456-7. - DOI
-
- Filek N., Cimadom A., Schulze C.H., Jäger H., Tebbich S. The impact of invasive plant management on the foraging ecology of the Warbler Finch (Certhidea olivacea) and the Small Tree Finch (Camarhynchus parvulus) on Galápagos. J. Ornithol. 2018;159:129–140. doi: 10.1007/s10336-017-1481-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doroftei M., Anastasiu P. Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Habitats and Their Effects on Invasive Plant Species in Danube Delta Biosphere Reserve, Romania. In: Rannow S., Neubert M., editors. Managing Protected Areas in Central and Eastern Europe Under Climate Change. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2014. pp. 267–278. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

