Novel Biomarkers Predictive of Diabetic Charcot Foot-An Overview of the Literature
- PMID: 36431079
- PMCID: PMC9698200
- DOI: 10.3390/life12111944
Novel Biomarkers Predictive of Diabetic Charcot Foot-An Overview of the Literature
Abstract
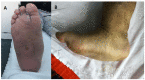
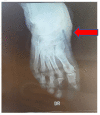
Background: Although Charcot diabetic foot (CDF) is a frequent complication of diabetic neuropathy, less is known about the possibility of its early prevention. Methods: A review of the original articles published in English, using the "biomarkers AND Charcot's foot" criterion, resulted in 33 articles from the PubMed database and seven articles from the Web of Science database. The five duplicates were eliminated, and two independent reviewers selected the most relevant articles, leaving a total of 21 articles. Results: The biomarkers identified are exhaustively described, related to the system of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and their soluble receptors (sRAGE), inflammatory cascade, osteoclastogenesis, and, respectively, osteoblastic activity. Conclusions: This article highlights the importance of potential early identifiable biomarkers that can lead to microstructural changes in the affected bones.
Keywords: Charcot diabetic foot; biomarkers; inflammation; neuropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Carro G.V., Saurral R., Witman E.L., Braver J.D., David R., Alterini P.A., Illuminati G., Carrió L.M., Torres J.C. Ataque de pie diabético. Descripción fisiopatológica, presentación clínica, tratamiento y evolución [Diabetic foot attack. Pathophysiological description, clinical presentation, treatment and outcomes] Med. (B Aires) 2020;80:523–530. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

