Aerospace Environmental Challenges for Electrical Insulation and Recent Developments for Electrified Aircraft
- PMID: 36431615
- PMCID: PMC9699481
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15228121
Aerospace Environmental Challenges for Electrical Insulation and Recent Developments for Electrified Aircraft
Abstract
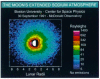
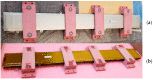
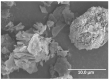
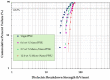
The growing trend towards high voltage electrical assets and propulsion in the aeronautics and space industry pose new challenges in electrical insulation materials that cannot be overlooked. Transition to new high voltage electrified systems with unprecedented high levels of voltage, power, and efficiency must be safe and reliable. Improvements in both performance and safety of megawatt power systems is complicated because of the need for additional power transmission wiring and cabling and new safety requirements that have the potential of making the resulting systems heavier. To mitigate this issue, novel lightweight materials and system solutions are required that would result in lower specific weights in the insulator and conductor. Although reduced size and weight of system components can be achieved with new concepts, designs, and technologies, the high voltage (≥300 V) operation presents a significant challenge. This challenge is further complicated when considering the extreme operating environment that is experienced in aircraft, spacecraft, and targeted human exploration destinations. This paper reviews the extreme environmental challenges for aerospace electrical insulation and the needs associated with operating under high voltage and extreme environments. It also examines several recently developed robust lightweight electrical insulation materials that could enhance insulation performance and life. In aerospace, research must consider mass when developing new technologies. The impact of these recent developments provides a pathway which could enable next generation high altitude all electric aircraft, lightweight power transmission cables for a future sustained presence on the Moon and missions to Mars using HV propulsion, such as spacecraft with Nuclear Electric Propulsion systems.
Keywords: Micro-Multilayered Multifunctional Electrical Insulation (MMEI); aerospace electrical insulation; electrical insulation composites; extreme environments; hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN); high voltage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Anderson C.D., Anderson J. Electric and Hybrid Cars: A history. 2nd ed. McFarland & Company, Inc.; Jefferson, NC, USA: 2010. p. 268.
-
- Dorrington G.E. Performance of battery-powered airships. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2007;221:91–104. doi: 10.1243/09544100JAERO41. - DOI
-
- Sahoo S., Zhao X., Kyprianidis K. A Review of Concepts, Benefits, and Challenges for Future Electrical Propulsion-Based Aircraft. Aerospace. 2020;7:44. doi: 10.3390/aerospace7040044. - DOI
-
- NASA Aeronautics Strategic Implementation Plan 2019 Update. NASA; Washington, DC, USA: 2019. p. 66.
-
- Madonna V., Giangrande P., Galea M. Electrical Power Generation in Aircraft: Review, Challenges, and Opportunities. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2018;4:646–659. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2018.2834142. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

