Analysis of Components and Properties of Extractives from Alnus cremastogyne Pods from Different Provenances
- PMID: 36431903
- PMCID: PMC9699184
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27227802
Analysis of Components and Properties of Extractives from Alnus cremastogyne Pods from Different Provenances
Abstract
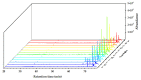
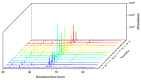
Chemical components with anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties extracted from Alnus bark and leaves have been extensively studied. However, less attention has been paid to extractives from Alnus pods, which are mostly treated as waste. Here, extractives of Alnus cremastogyne pods from 12 provenances in Sichuan Province were studied for high value-added utilization of Alnus waste. The extractives were analyzed by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometer (GC-MS), Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis spectra), and 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) scavenging activity. A total of 58, 49, and 51 chemical components were found when the organic solvents of ethanol, petroleum ether, and ethyl acetate were used to collect extractives, respectively. These chemical components including Phytol, CIS-5,8,11,14,17-eicosapentaenoic acid, Germacrene D, Lupeol, and β-sitosterol, etc., have wide applications in the fields of pharmacy and cosmetics. Moreover, it was also found that extractives in ethanol and ethyl acetate had impressive UV resistance, especially for UV-C and UV-B blocking. The results showed that the maximum block ratio towards UV-C and UV-B could reach 99%. In addition, the ethanol extract showed good anti-oxidant activity with a maximum free radical scavenging rate of 96.19%. This comprehensive and systematic study on extractives from Alnus cremastogyne pods promotes the development of high-value utilization of Alnus components.
Keywords: Alnus cremastogyne pods; UV absorbability; anti-oxidant activity; extractives.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Phenotypic Variation Analysis and Excellent Clone Selection of Alnus cremastogyne from Different Provenances.Plants (Basel). 2023 Sep 13;12(18):3259. doi: 10.3390/plants12183259. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765423 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro pro-inflammatory enzyme inhibition and anti-oxidant potential of selected Sri Lankan medicinal plants.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Oct 3;18(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2335-1. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 30285710 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical and biological studies on Alnus glutinosa subsp. glutinosa, A. orientalis var. orientalis and A. orientalis var. pubescens leaves.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Nov 4;192:148-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.07.007. Epub 2016 Jul 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27381042
-
In vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of extracts from Potentilla recta and its main ellagitannin, agrimoniin.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Aug 26;149(1):222-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.026. Epub 2013 Jun 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23811215
-
Investigations on anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of Alnus nitida Spach (Endl). stem bark in Sprague Dawley rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Feb 23;198:407-416. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.041. Epub 2017 Jan 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28119101
Cited by
-
Phenotypic Variation Analysis and Excellent Clone Selection of Alnus cremastogyne from Different Provenances.Plants (Basel). 2023 Sep 13;12(18):3259. doi: 10.3390/plants12183259. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765423 Free PMC article.
-
Breynia cernua: Chemical Profiling of Volatile Compounds in the Stem Extract and Its Antioxidant, Antibacterial, Antiplasmodial and Anticancer Activity In Vitro and In Silico.Metabolites. 2023 Feb 15;13(2):281. doi: 10.3390/metabo13020281. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36837900 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kirker G.T., Blodgett A.B., Arango R.A., Lebow P.K., Clausen C.A. The role of extractives in naturally durable wood species. Int. Biodeteri. Biodegr. 2013;82:53–58. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.03.007. - DOI
-
- Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae. [(accessed on 10 November 2022)]. Available online: http://www.iplant.cn/info/Alnus.
-
- Bühlmann T., Caprez R., Hiltbrunner E., Körner C., Niklaus P.A. Nitrogen fixation by Alnus species boosts soil nitrous oxide emissions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017;68:740–748. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12457. - DOI
-
- Liu L., Wang R., Zhang Y., Mou Q., Gou Y., Liu K., Huang N., Ouyang C., Hu J., Du B. Simulation of potential suitable distribution of Alnus cremastogyne Burk. In China under climate change scenarios. Ecol. Indic. 2021;133:108396. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108396. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

