A Comprehensive Study of N-Butyl-1H-Benzimidazole
- PMID: 36431965
- PMCID: PMC9698437
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27227864
A Comprehensive Study of N-Butyl-1H-Benzimidazole
Abstract
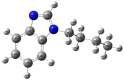
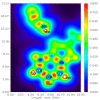
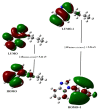
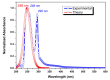
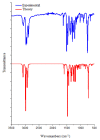
Imidazole derivatives have found wide application in organic and medicinal chemistry. In particular, benzimidazoles have proven biological activity as antiviral, antimicrobial, and antitumor agents. In this work, we experimentally and theoretically investigated N-Butyl-1H-benzimidazole. It has been shown that the presence of a butyl substituent in the N position does not significantly affect the conjugation and structural organization of benzimidazole. The optimized molecular parameters were performed by the DFT/B3LYP method with 6-311++G(d,p) basis set. This level of theory shows excellent concurrence with the experimental data. The non-covalent interactions that existed within our compound N-Butyl-1H-benzimidazole were also analyzed by the AIM, RDG, ELF, and LOL topological methods. The color shades of the ELF and LOL maps confirm the presence of bonding and non-bonding electrons in N-Butyl-1H-benzimidazole. From DFT calculations, various methods such as molecular electrostatic potential (MEP), Fukui functions, Mulliken atomic charges, and frontier molecular orbital (HOMO-LUMO) were characterized. Furthermore, UV-Vis absorption and natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis were calculated. It is shown that the experimental and theoretical spectra of N-Butyl-1H-benzimidazole have a peak at 248 nm; in addition, the experimental spectrum has a peak near 295 nm. The NBO method shows that the delocalization of the aσ-electron from σ (C1-C2) is distributed into antibonding σ* (C1-C6), σ* (C1-N26), and σ* (C6-H11), which leads to stabilization energies of 4.63, 0.86, and 2.42 KJ/mol, respectively. Spectroscopic investigations of N-Butyl-1H-benzimidazole were carried out experimentally and theoretically to find FTIR vibrational spectra.
Keywords: AIM; DFT; ELF; N-butyl-1H-benzimidazole; RDG; benzimidazole.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Pathare B., Bansode T. Review- biological active benzimidazole derivatives. Results Chem. 2021;3:100200. doi: 10.1016/j.rechem.2021.100200. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

