Sequence-Activity Relationship of ATCUN Peptides in the Context of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 36432004
- PMCID: PMC9698028
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27227903
Sequence-Activity Relationship of ATCUN Peptides in the Context of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
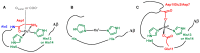
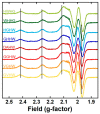
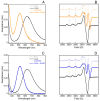
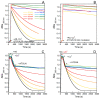
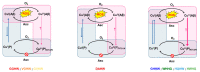
Amino-terminal CuII and NiII (ATCUN) binding sequences are widespread in the biological world. Here, we report on the study of eight ATCUN peptides aimed at targeting copper ions and stopping the associated formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). This study was actually more focused on Cu(Aβ)-induced ROS production in which the Aβ peptide is the "villain" linked to Alzheimer's disease. The full characterization of CuII binding to the ATCUN peptides, the CuII extraction from CuII(Aβ), and the ability of the peptides to prevent and/or stop ROS formation are described in the relevant biological conditions. We highlighted in this research that all the ATCUN motifs studied formed the same thermodynamic complex but that the addition of a second histidine in position 1 or 2 allowed for an improvement in the CuII uptake kinetics. This kinetic rate was directly related to the ability of the peptide to stop the CuII(Aβ)-induced production of ROS, with the most efficient motifs being HWHG and HGHW.
Keywords: ATCUN peptide; copper; kinetics; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
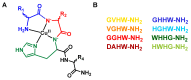



Similar articles
-
Unlocking Cu(I)-Mediated Catalytic Pathways for Efficient ROS Generation by Incorporating an Oxazole-Based Histidine Surrogate into Cu(II)-ATCUN Complexes.Inorg Chem. 2023 Jul 3;62(26):10279-10290. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c01084. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Inorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 37342900
-
Using N-Terminal Coordination of Cu(II) and Ni(II) to Isolate the Coordination Environment of Cu(I) and Cu(II) Bound to His13 and His14 in Amyloid-β(4-16).Inorg Chem. 2019 Nov 18;58(22):15138-15154. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01940. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Inorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31657204
-
Why the Ala-His-His Peptide Is an Appropriate Scaffold to Remove and Redox Silence Copper Ions from the Alzheimer's-Related Aβ Peptide.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 20;12(10):1327. doi: 10.3390/biom12101327. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36291536 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of Cu(II) complexation by ATCUN/NTS and related peptides: a gold mine of novel ideas for copper biology.Dalton Trans. 2021 Dec 20;51(1):14-26. doi: 10.1039/d1dt02878b. Dalton Trans. 2021. PMID: 34816848 Review.
-
Abeta-mediated ROS production by Cu ions: structural insights, mechanisms and relevance to Alzheimer's disease.Biochimie. 2009 Oct;91(10):1212-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2009.03.013. Epub 2009 Mar 28. Biochimie. 2009. PMID: 19332103 Review.
Cited by
-
Peptide-based amyloid-beta aggregation inhibitors.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Dec 31. doi: 10.1039/d4md00729h. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39882170 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dementia Statistics. [(accessed on 1 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.alzint.org/about/dementia-facts-figures/dementia-statistics/
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Facts & Figures. [(accessed on 1 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.brightfocus.org/alzheimers/article/alzheimers-disease-facts-....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

