Enhancement of Anti-Tumoral Properties of Paclitaxel Nano-Crystals by Conjugation of Folic Acid to Pluronic F127: Formulation Optimization, In Vitro and In Vivo Study
- PMID: 36432014
- PMCID: PMC9696646
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27227914
Enhancement of Anti-Tumoral Properties of Paclitaxel Nano-Crystals by Conjugation of Folic Acid to Pluronic F127: Formulation Optimization, In Vitro and In Vivo Study
Abstract
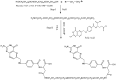
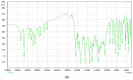
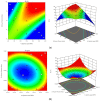
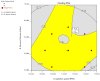
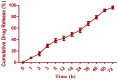
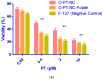
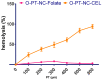
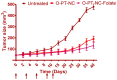
A brand-new nano-crystal (NC) version of the hydrophobic drug Paclitaxel (PT) were formulated for cancer treatment. A stable NC formulation for the administration of PT was created using the triblock co-polymer Pluronic F127. To achieve maximum entrapment effectiveness and minimal particle size, the formulation was improved using the central composite design by considering agitation speed and vacuum pressure at five levels (coded as +1.414, +1, 0, -1, and -1.414). According to the Design Expert software's predictions, 13 runs were created and evaluated for the chosen responses. The formulation prepared with an agitation speed of 1260 RPM and a vacuum pressure of 77.53 mbar can meet the requirements of the ideal formulation in order to achieve 142.56 nm of PS and 75.18% EE, according to the level of desirability (D = 0.959). Folic acid was conjugated to Pluronic F127 to create folate receptor-targeted NC. The drug release profile of the nano-crystals in vitro demonstrated sustained release over an extended period. Folate receptor (FR)-targeted NC (O-PT-NC-Folate) has also been prepared by conjugating folic acid to Pluronic F127. MTT test is used to validate the targeting efficacy on the FR-positive human oral cancer cell line (KB). At pharmacologically relevant concentrations, the PT nano-crystal formulation did not cause hemolysis. Compared to non-targeted NC of PT, the O-PT-NC-Folate showed a comparable but more sustained anti-cancer effect, according to an in vivo anti-tumor investigation in NCI/ADR-RES cell lines. The remarkable anti-tumor effectiveness, minimal toxicity, and simplicity of scale-up manufacturing of the NC formulations indicate their potential for clinical development. Other hydrophobic medications that are formulated into nano-systems for improved therapy may benefit from the formulation approach.
Keywords: Paclitaxel; anti-cancer; central composite design; nano-crystals; optimization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The targeting properties of folate-conjugated Pluronic F127/poly (lactic-co-glycolic) nanoparticles.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Dec;105(Pt 1):711-719. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.07.085. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. PMID: 28716749
-
Folate-conjugated pluronic/polylactic acid polymersomes for oral delivery of paclitaxel.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Oct 15;139:377-386. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.07.224. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 31377294
-
Redox-responsive F127-folate/F127-disulfide bond-d-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate/P123 mixed micelles loaded with paclitaxel for the reversal of multidrug resistance in tumors.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Feb 7;13:805-830. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S152395. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29445276 Free PMC article.
-
Transferrin/folate dual-targeting Pluronic F127/poly(lactic acid) polymersomes for effective anticancer drug delivery.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2022 Jun;33(9):1140-1156. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2022.2044434. Epub 2022 Feb 25. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2022. PMID: 35179085
-
A SWOT analysis of nano co-crystals in drug delivery: present outlook and future perspectives.RSC Adv. 2023 Mar 7;13(11):7339-7351. doi: 10.1039/d3ra00161j. eCollection 2023 Mar 1. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36895773 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design and evaluation of magnetic-targeted bilosomal gel for rheumatoid arthritis: flurbiprofen delivery using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 23;15:1433734. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1433734. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39246659 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of antifungal activity and transdermal delivery of 5-flucytosine via tailored spanlastic nanovesicles: statistical optimization, in-vitro characterization, and in-vivo biodistribution study.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 4;14:1321517. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1321517. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38125883 Free PMC article.
-
Use of customized 3-dimensional printed mandibular prostheses with a dental implant pressure-reducing device in mandibular body defect: A finite element study performing multiresponse surface methodology.J Dent Sci. 2024 Jan;19(1):502-514. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2023.09.011. Epub 2023 Sep 22. J Dent Sci. 2024. PMID: 38303793 Free PMC article.
-
Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Powered Formulation Development, Optimization and Evaluation of Thiolated Based Mucoadhesive Nanocrystals for Local Delivery of Simvastatin.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Nov 28;14(23):5184. doi: 10.3390/polym14235184. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501579 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemicals and Cancer Treatment: Cell-Derived and Biomimetic Vesicles as Promising Carriers.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 9;15(5):1445. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051445. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. [(accessed on 1 July 2022)]. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/
-
- Hollis C.P., Li T. Pharmaceutical Sciences Encyclopedia. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2013. Nanocrystals Production, Characterization, and Application for Cancer Therapy.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

