Oxidative [3+2]Cycloaddition of Alkynylphosphonates with Heterocyclic N-Imines: Synthesis of Pyrazolo[1,5- a]Pyridine-3-phosphonates
- PMID: 36432015
- PMCID: PMC9694626
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27227913
Oxidative [3+2]Cycloaddition of Alkynylphosphonates with Heterocyclic N-Imines: Synthesis of Pyrazolo[1,5- a]Pyridine-3-phosphonates
Abstract
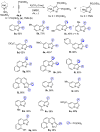
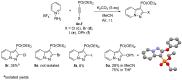
A series of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine-3-ylphosphonates were prepared with moderate to good yields by the oxidative [3+2]cycloaddition of 2-subtituted ethynylphosphonates with in situ generated pyridinium-N-imines and their annulated analogs. 2-Aliphatic and 2-Ph acetylenes demonstrate low activity, and the corresponding pyrazolopyridines were achieved with a moderate yield in the presence of 10 mol% Fe(NO3)3·9H2O. At the same time, tetraethyl ethynylbisphosphonate, diethyl 2-TMS- and 2-OPh-ethynylphosphonates possess much greater reactivity and the corresponding pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridines, and their annulated derivatives were obtained with good to excellent yields without any catalyst. 2-Halogenated ethynylphosphonates also readily reacted with pyridinium-N-imines, forming complex mixtures containing poor amounts of 2-halogenated pyrazolopyridines.
Keywords: alkynes; cycloaddition; heterocycles; iron; oxidation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Copper-mediated oxidative [3 + 2]-annulation of nitroalkenes and pyridinium imines: efficient synthesis of 3-fluoro- and 3-nitro-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridines.Org Biomol Chem. 2020 Feb 19;18(7):1436-1448. doi: 10.1039/c9ob02668a. Org Biomol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32022079
-
Pyridine-phosphinimine ligand-accelerated Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition for preparation of 1-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,3-triazole derivatives.Org Biomol Chem. 2014 Aug 21;12(31):5954-63. doi: 10.1039/c4ob01176g. Org Biomol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24984611
-
Development of a tailor-made bis(oxazolidine)pyridine-metal catalyst for the [3+2] cycloaddition of azomethine imines with propiolates.Chem Commun (Camb). 2013 Sep 14;49(71):7776-8. doi: 10.1039/c3cc44354j. Chem Commun (Camb). 2013. PMID: 23900514
-
A review on the assembly of multi-substituted pyridines via Co-catalyzed [2 + 2 + 2] cycloaddition with nitriles.Org Biomol Chem. 2022 Sep 28;20(37):7391-7404. doi: 10.1039/d2ob01344d. Org Biomol Chem. 2022. PMID: 36098263 Review.
-
Generation of N-Heterocycles via Tandem Reactions of N '-(2-Alkynylbenzylidene)hydrazides.Chem Rec. 2016 Feb;16(1):19-34. doi: 10.1002/tcr.201500219. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Chem Rec. 2016. PMID: 26493018 Review.
Cited by
-
One-Pot Phosphonylation of Heteroaromatic Lithium Reagents: The Scope and Limitations of Its Use for the Synthesis of Heteroaromatic Phosphonates.Molecules. 2023 Mar 31;28(7):3135. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073135. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049896 Free PMC article.
-
Copper-Catalyzed Asymmetric Dearomative [3+2] Cycloaddition of Nitroheteroarenes with Azomethines.Molecules. 2023 Mar 19;28(6):2765. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062765. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985737 Free PMC article.
-
Recent highlights in the synthesis and biological significance of pyrazole derivatives.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 9;10(20):e38894. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38894. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39492900 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nakao S., Nogami M., Iwatani M., Imaeda T., Ito M., Tanaka T., Tawada M., Endo S., Cary D.R., Ohori M., et al. Identification of a Selective DDX3X Inhibitor with Newly Developed Quantitative High-Throughput RNA Helicase Assays. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020;523:795–801. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.12.094. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

