Comprehensive Metabolite Profiling of Four Different Beans Fermented by Aspergillus oryzae
- PMID: 36432017
- PMCID: PMC9695057
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27227917
Comprehensive Metabolite Profiling of Four Different Beans Fermented by Aspergillus oryzae
Abstract
Fermented bean products are used worldwide; most of the products are made using only a few kinds of beans. However, the metabolite changes and contents in the beans generally used during fermentation are unrevealed. Therefore, we selected four different beans (soybean, Glycine max, GM; wild soybean, Glycine soja, GS; common bean, Phaseolus vulgaris, PV; and hyacinth bean, Lablab purpureus, LP) that are the most widely consumed and fermented with Aspergillus oryzae. Then, metabolome and multivariate statistical analysis were performed to figure out metabolite changes during fermentation. In the four beans, carbohydrates were decreased, but amino acids and fatty acids were increased in the four beans as they fermented. The relative amounts of amino acids were relatively abundant in fermented PV and LP as compared to other beans. In contrast, isoflavone aglycones (e.g., daidzein, glycitein, and genistein) and DDMP-conjugated soyasaponins (e.g., soyasaponins βa and γg) were increased in GM and GS during fermentation. Notably, these metabolite changes were more significant in GS than GM. In addition, the increase of antioxidant activity in fermented GS was significant compared to other beans. We expect our research provides a basis to extend choice for bean fermentation for consumers and food producers.
Keywords: Aspergillus oryzae; antioxidant activity; beans; fermentation; metabolite profiling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
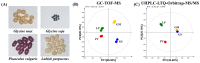
 (GM): G. max,
(GM): G. max,  (GS): G. soja,
(GS): G. soja,  (PV): P. vulgaris,
(PV): P. vulgaris,  (LP): L. purpureus).
(LP): L. purpureus).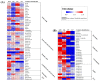
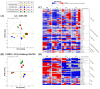
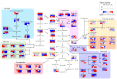
 (GM): G. max,
(GM): G. max,  (GS): G. soja,
(GS): G. soja,  (PV): P. vulgaris,
(PV): P. vulgaris,  (LP): L. purpureus, 0D: 0 day of fermentation, 1D: 1 day after fermentation, 2D: 2 days after fermentation, 3D: 3 days after fermentation.
(LP): L. purpureus, 0D: 0 day of fermentation, 1D: 1 day after fermentation, 2D: 2 days after fermentation, 3D: 3 days after fermentation.Similar articles
-
Simultaneous enhancement of free isoflavone content and antioxidant potential of soybean by fermentation with Aspergillus oryzae.J Food Sci. 2011 Oct;76(8):H194-200. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02350.x. J Food Sci. 2011. PMID: 22417591
-
Distribution profiles of isoflavone isomers in black bean kojis prepared with various filamentous fungi.J Agric Food Chem. 2006 Feb 22;54(4):1309-14. doi: 10.1021/jf058139m. J Agric Food Chem. 2006. PMID: 16478253
-
Targeted metabolomics for Aspergillus oryzae-mediated biotransformation of soybean isoflavones, showing variations in primary metabolites.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2014;78(1):167-74. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2014.877827. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 25036500
-
Fathoming Aspergillus oryzae metabolomes in formulated growth matrices.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2019 Feb;39(1):35-49. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2018.1490246. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30037282 Review.
-
An underutilized bean: hyacinth bean [Lablab purpureus (L.) sweet]: bioactive compounds, functional activity, and future food prospect and applications.J Sci Food Agric. 2025 Jan 30;105(2):701-720. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13708. Epub 2024 Jul 3. J Sci Food Agric. 2025. PMID: 38961686 Review.
Cited by
-
NMR-Based Metabolomic Study on Phaseolus vulgaris Flour Fermented by Lactic Acid Bacteria and Yeasts.Molecules. 2023 Jun 20;28(12):4864. doi: 10.3390/molecules28124864. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37375419 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant capacities and non-volatile metabolites changes after solid-state fermentation of soybean using oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) mycelium.Front Nutr. 2024 Dec 6;11:1509341. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1509341. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39713777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sadh P.K., Saharan P., Duhan J.S. Bio-augmentation of antioxidants and phenolic content of Lablab purpureus by solid state fermentation with GRAS filamentous fungi. Resour. Technol. 2017;3:285–292. doi: 10.1016/j.reffit.2016.12.007. - DOI
-
- De Almeida Costa G.E., Da Silva Queiroz-Monici K., Pissini Machado Reis S.M., De Oliveira A.C. Chemical composition, dietary fibre and resistant starch contents of raw and cooked pea, common bean, chickpea and lentil legumes. Food Chem. 2006;94:327–330. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.11.020. - DOI
-
- Song D.H., Chun B.H., Lee S., Son S.Y., Reddy C.K., Mun H.I., Jeon C.O., Lee C.H. Comprehensive metabolite profiling and microbial communities of Doenjang (fermented soy paste) and Ganjang (fermented soy sauce): A comparative study. Foods. 2021;10:641. doi: 10.3390/foods10030641. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

