A New Therapeutic Trend: Natural Medicine for Ameliorating Ischemic Stroke via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 36432062
- PMCID: PMC9694461
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27227963
A New Therapeutic Trend: Natural Medicine for Ameliorating Ischemic Stroke via PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
Abstract
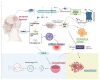
Ischemic stroke (IS) is an acute cerebrovascular disease caused by sudden arterial occlusion, which is characterized by a high morbidity, mortality, and disability rate. It is one of the most important causes of nervous system morbidity and mortality in the world. In recent years, the search for new medicine for the treatment of IS has become an attractive research focus. Due to the extremely limited time window of traditional medicine treatment, some side effects may occur, and accompanied by the occurrence of adverse reactions, the frequency of exploration with natural medicine is significantly increased. Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) signaling pathway is a classical pathway for cell metabolism, growth, apoptosis, and other physiological activities. There is considerable research on medicine that treats various diseases through this pathway. This review focuses on how natural medicines (including herbs and insects) regulate important pathophysiological processes such as inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, and the role it plays in improving IS. We found that many kinds of herbal medicine and insect medicine can alleviate the damage caused by IS through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Moreover, the prescription after their combination can also achieve certain results. Therefore, this review provides a new candidate category for medicine development in the treatment of IS.
Keywords: PI3K/Akt signaling pathway; ischemic stroke; natural medicine; new trend; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advances of phytotherapy in ischemic stroke targeting PI3K/Akt signaling.Phytother Res. 2023 Dec;37(12):5509-5528. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7994. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Phytother Res. 2023. PMID: 37641491 Review.
-
Proteomics-Guided Study on Buyang Huanwu Decoction for Its Neuroprotective and Neurogenic Mechanisms for Transient Ischemic Stroke: Involvements of EGFR/PI3K/Akt/Bad/14-3-3 and Jak2/Stat3/Cyclin D1 Signaling Cascades.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Oct;57(10):4305-4321. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02016-y. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32700252
-
CXCL8 gene silencing promotes neuroglial cells activation while inhibiting neuroinflammation through the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB-signaling pathway in mice with ischemic stroke.J Cell Physiol. 2019 May;234(5):7341-7355. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27493. Epub 2018 Oct 26. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30362547
-
A diarylheptanoid compound from Alpinia officinarum Hance ameliorates high glucose-induced insulin resistance by regulating PI3K/AKT-Nrf2-GSK3β signaling pathways in HepG2 cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Sep 15;295:115397. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115397. Epub 2022 May 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35605918
-
The pharmacological effects of Berberine and its therapeutic potential in different diseases: Role of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signaling pathway.Phytother Res. 2024 Jan;38(1):349-367. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8040. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 37922566 Review.
Cited by
-
Revealing the pharmacological mechanisms of nao-an dropping pill in preventing and treating ischemic stroke via the PI3K/Akt/eNOS and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways.Sci Rep. 2024 May 16;14(1):11240. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61770-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38755191 Free PMC article.
-
Nobiletin alleviates brain injury in uremic mice and inhibits indoxyl sulfate-induced neurotoxicity in HT22 cells through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathway.Cytojournal. 2025 Mar 3;22:27. doi: 10.25259/Cytojournal_233_2024. eCollection 2025. Cytojournal. 2025. PMID: 40260073 Free PMC article.
-
10% carbon dioxide improves cognitive function after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats: inhibiting neuronal apoptosis through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Med Gas Res. 2025 Sep 1;15(3):391-397. doi: 10.4103/mgr.MEDGASRES-D-24-00116. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Med Gas Res. 2025. PMID: 40072264 Free PMC article.
-
Scutellarin Alleviates Neuronal Apoptosis in Ischemic Stroke via Activation of the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 28;26(5):2175. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052175. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076795 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Network Pharmacology in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases with Traditional Chinese Medicine.Planta Med. 2025 Apr;91(5):226-237. doi: 10.1055/a-2512-8928. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Planta Med. 2025. PMID: 39778593 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benjamin E.J., Muntner P., Alonso A., Bittencourt M.S., Callaway C.W., Carson A.P., Chamberlain A.M., Chang A.R., Cheng S., Das S.R., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:e56–e528. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Oates C.P., Bienstock S.W., Miller M., Giustino G., Danilov T., Kukar N., Kocovic N., Sperling D., Singh R., Benhuri D., et al. Using Clinical and Echocardiographic Characteristics to Characterize the Risk of Ischemic Stroke in Patients with COVID-19. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022;31:106217. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.106217. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

