Structure-Activity Relationship Studies Based on 3D-QSAR CoMFA/CoMSIA for Thieno-Pyrimidine Derivatives as Triple Negative Breast Cancer Inhibitors
- PMID: 36432075
- PMCID: PMC9698756
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27227974
Structure-Activity Relationship Studies Based on 3D-QSAR CoMFA/CoMSIA for Thieno-Pyrimidine Derivatives as Triple Negative Breast Cancer Inhibitors
Abstract
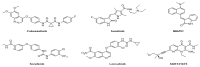
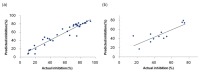
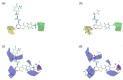
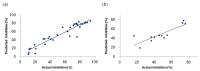
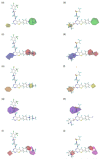
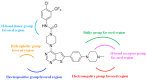
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is defined as a kind of breast cancer that lacks estrogen receptors (ER), progesterone receptors (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptors (HER2). This cancer accounts for 10-15% of all breast cancers and has the features of high invasiveness and metastatic potential. The treatment regimens are still lacking and need to develop novel inhibitors for therapeutic strategies. Three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (3D-QSAR) analyses, based on a series of forty-seven thieno-pyrimidine derivatives, were performed to identify the key structural features for the inhibitory biological activities. The established comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) presented a leave-one-out cross-validated correlation coefficient q2 of 0.818 and a determination coefficient r2 of 0.917. In comparative molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA), a q2 of 0.801 and an r2 of 0.897 were exhibited. The predictive capability of these models was confirmed by using external validation and was further validated by the progressive scrambling stability test. From these results of validation, the models were determined to be statistically reliable and robust. This study could provide valuable information for further optimization and design of novel inhibitors against metastatic breast cancer.
Keywords: 3D-QSAR; CoMFA; CoMSIA; TNBC; VEGFR3; thieno-pyrimidine derivatives.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
3D QSAR pharmacophore, CoMFA and CoMSIA based design and docking studies on phenyl alkyl ketones as inhibitors of phosphodiesterase 4.Med Chem. 2012 Sep;8(5):894-912. doi: 10.2174/157340612802084298. Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22741782
-
In silico design of novel FAK inhibitors using integrated molecular docking, 3D-QSAR and molecular dynamics simulation studies.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Aug;40(13):5965-5982. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1875880. Epub 2021 Jan 21. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 33475043
-
Docking-based 3D-QSAR study of pyridyl aminothiazole derivatives as checkpoint kinase 1 inhibitors.SAR QSAR Environ Res. 2014;25(8):651-71. doi: 10.1080/1062936X.2014.923040. Epub 2014 Jun 9. SAR QSAR Environ Res. 2014. PMID: 24911214
-
3D QSAR and molecular docking studies of benzimidazole derivatives as hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitors.J Chem Inf Model. 2008 Jan;48(1):42-55. doi: 10.1021/ci700266z. Epub 2007 Dec 13. J Chem Inf Model. 2008. PMID: 18076152
-
Molecular docking and 3D-QSAR study on 4-(1H-indazol-4-yl) phenylamino and aminopyrazolopyridine urea derivatives as kinase insert domain receptor (KDR) inhibitors.J Mol Model. 2012 Mar;18(3):1207-18. doi: 10.1007/s00894-011-1146-9. Epub 2011 Jun 22. J Mol Model. 2012. PMID: 21695506
Cited by
-
Design, Synthesis, Herbicidal Activity, and Structure-Activity Relationship Study of Novel 6-(5-Aryl-Substituted-1-Pyrazolyl)-2-Picolinic Acid as Potential Herbicides.Molecules. 2023 Feb 2;28(3):1431. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031431. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36771096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suleman M., Tahir Ul Qamar M., Saleem S., Ahmad S., Ali S.S., Khan H., Akbar F., Khan W., Alblihy A., Alrumaihi F., et al. Mutational Landscape of Pirin and Elucidation of the Impact of Most Detrimental Missense Variants that Accelerate the Breast Cancer Pathways: A Computational Modelling Study. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021;8:692835. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.692835. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. [(accessed on 26 March 2021)]. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer.
-
- Ensenyat-Mendez M., Llinàs-Arias P., Orozco J.I.J., Iñiguez-Muñoz S., Salomon M.P., Sesé B., DiNome M.L., Marzese D.M. Current Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Subtypes: Dissecting the Most Aggressive Form of Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021;11:681476. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.681476. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

