Tricyano-Methylene-Pyridine Based High-Performance Aggregation-Induced Emission Photosensitizer for Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy
- PMID: 36432090
- PMCID: PMC9697965
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27227981
Tricyano-Methylene-Pyridine Based High-Performance Aggregation-Induced Emission Photosensitizer for Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy
Abstract
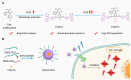
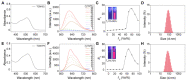
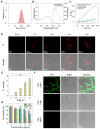
Photosensitizers equipped with high reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation capability and bright emission are essential for accurate tumor imaging and precise photodynamic therapy (PDT). However, traditional aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ) photosensitizers cannot simultaneously produce desirable ROS and bright fluorescence, resulting in poor image-guided therapy effect. Herein, we report an aggregation-induced emission (AIE) photosensitizer TCM-Ph with a strong donor-π-acceptor (D-π-A) structure, which greatly separates the HOMO-LUMO distribution and reduces the ΔEST, thereby increasing the number of triplet excitons and producing more ROS. The AIE photosensitizer TCM-Ph has bright near-infrared emission, as well as a higher ROS generation capacity than the commercial photosensitizers Bengal Rose (RB) and Chlorine e6 (Ce6), and can effectively eliminate cancer cells under image guidance. Therefore, the AIE photosensitizer TCM-Ph has great potential to replace the commercial photosensitizers.
Keywords: ROS generation; aggregation-induced emission; bioimaging; photosensitizer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang Y., Zhao X., Li Y., Wang X., Wang Q., Lu H., Zhu L. A fluorescent photosensitizer with far red/near-infrared aggregation-induced emission for imaging and photodynamic killing of bacteria. Dyes Pigments. 2019;165:53–57. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2019.02.019. - DOI
-
- Xu W., Zhang Z., Kang M., Guo H., Li Y., Wen H., Lee M.M.S., Wang Z., Kwok R.T.K., Lam J.W.Y., et al. Making the best use of excited-state energy: Multimodality theranostic systems based on second near-infrared (NIR-II) aggregation-induced emission luminogens (AIEgens) ACS Mater. Lett. 2020;2:1033–1040. doi: 10.1021/acsmaterialslett.0c00263. - DOI
-
- Wang D., Su H., Kwok R.T.K., Shan G., Leung A.C.S., Lee M.M.S., Sung H.H.Y., Williams I.D., Lam J.W.Y., Tang B.Z. Facile synthesis of red/NIR AIE luminogens with simple structures, bright emissions, and high photostabilities, and their applications for specific imaging of lipid droplets and image-guided photodynamic therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017;27:1704039. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201704039. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 22222803/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 91959202/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 21974047/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2018SHZDZX03/Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project
- 2021YFA0910000/National Key Research and Development Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

