Antibacterial Screening of Isoespintanol, an Aromatic Monoterpene Isolated from Oxandra xylopioides Diels
- PMID: 36432105
- PMCID: PMC9692887
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27228004
Antibacterial Screening of Isoespintanol, an Aromatic Monoterpene Isolated from Oxandra xylopioides Diels
Abstract
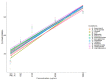
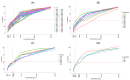
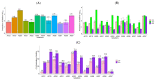
The incidence of nosocomial infections, as well as the high mortality and drug resistance expressed by nosocomial pathogens, especially in immunocompromised patients, poses significant medical challenges. Currently, the efficacy of plant compounds with antimicrobial potential has been reported as a promising alternative therapy to traditional methods. Isoespintanol (ISO) is a monoterpene with high biological activity. Using the broth microdilution method, the antibacterial activity of ISO was examined in 90 clinical isolates, which included 14 different species: (Escherichia coli (38), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (12), Klebsiella pneumoniae (13), Acinetobacter baumannii (3), Proteus mirabilis (7), Staphylococcus epidermidis (3), Staphylococcus aureus (5), Enterococcus faecium (1), Enterococcus faecalis (1), Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (2), Citrobacter koseri (2), Serratia marcescens (1), Aeromonas hydrophila (1), and Providencia rettgeri (1). MIC90 minimum inhibitory concentration values ranged from 694.3 to 916.5 µg/mL and MIC50 values from 154.2 to 457.3 µg/mL. The eradication of mature biofilms in P. aeruginosa after 1 h of exposure to ISO was between 6.6 and 77.4%, being higher in all cases than the percentage of biofilm eradication in cells treated with ciprofloxacin, which was between 4.3 and 67.5%. ISO has antibacterial and antibiofilm potential against nosocomial bacteria and could serve as an adjuvant in the control of these pathogens.
Keywords: Oxandra xylopioides; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; antibacterial activity; antibiofilms; isoespintanol; nosocomial infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antifungal potential of isoespintanol extracted from Oxandra xylopioides diels (Annonaceae) against intrahospital isolations of Candida SPP.Heliyon. 2022 Oct 18;8(10):e11110. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11110. eCollection 2022 Oct. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36303897 Free PMC article.
-
[Post-marketing surveillance of antibacterial activities of cefozopran against various clinical isolates--II. Gram-negative bacteria].Jpn J Antibiot. 2002 Feb;55(1):22-60. Jpn J Antibiot. 2002. PMID: 11977920 Japanese.
-
Update of incidence and antimicrobial susceptibility trends of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from Chinese intra-abdominal infection patients.BMC Infect Dis. 2017 Dec 18;17(1):776. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2873-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 29254478 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Antifungal Action of Monoterpene Isoespintanol against Clinical Isolates of Candida tropicalis.Molecules. 2022 Sep 8;27(18):5808. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185808. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144544 Free PMC article.
-
Sulopenem: An Intravenous and Oral Penem for the Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections Due to Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria.Drugs. 2022 Apr;82(5):533-557. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01688-1. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35294769 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing tomato plant immune responses to Fusarium wilt disease by red seaweed Jania sp.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 5;14(1):18052. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67233-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39103395 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Antifungal Effect and In Vivo Toxicity of a Monoterpene Isoespintanol Obtained from Oxandra xylopioides Diels.Molecules. 2024 Sep 17;29(18):4417. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184417. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339412 Free PMC article.
-
Isoespintanol Antifungal Activity Involves Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Inhibition of Biofilm Formation, and Damage to Cell Wall Integrity in Candida tropicalis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 15;24(12):10187. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210187. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373346 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic Potential of the Monoterpene Isoespintanol against Human Tumor Cell Lines.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 23;25(9):4614. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094614. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suksatan W., Jasim S.A., Widjaja G., Jalil A.T., Chupradit S., Ansari M.J., Mustafa Y.F., Hammoodi H.A., Mohammadi M.J. Assessment effects and risk of nosocomial infection and needle sticks injuries among patents and health care worker. Toxicol. Rep. 2022;9:284–292. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.02.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aman S., Mittal D., Shriwastav S., Tuli H.S., Chauhan S., Singh P., Sharma S., Saini R.V., Kaur N., Saini A.K. Prevalence of multidrug-resistant strains in device associated nosocomial infection and their in vitro killing by nanocomposites. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022;78:103687. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103687. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

