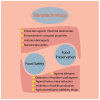
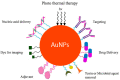
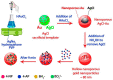
Role of AuNPs in Active Food Packaging Improvement: A Review
- PMID: 36432128
- PMCID: PMC9696957
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27228027
Role of AuNPs in Active Food Packaging Improvement: A Review
Abstract
There is a worldwide concern about food loss due to reduced shelf life among food science researchers. Hence, it seems that any techniques contributing to improved food packaging are most welcome in the food sector. It has been demonstrated that the administration of nanotechnology-based techniques such as metal-based nanoparticles can fade away the unresolved obstacles in shortened shelf life and environmental concerns. Along with substantial signs of progress in nanoscience, there is a great interest in the usage of green synthesis-based methods for gold nanoparticles as the most advantageous metals, when compared to conventional chemistry-based methods. Interestingly, those aforementioned methods have significant potential to simplify targeted administration of gold nanoparticles due to a large surface-volume ratio, and diminished biohazards, aimed at increasing stability, and induction of anti-microbial or antioxidant properties. However, it is necessary to consider the hazards of gold nanoparticles including migration for food packaging purposes.
Keywords: antimicrobial effects; food packaging; gold nanoparticles; nanotechnology; shelf life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inorganic and metal nanoparticles and their antimicrobial activity in food packaging applications.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2018 Mar;44(2):161-181. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2017.1332001. Epub 2017 Jun 3. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 28578640 Review.
-
Metal-Based Nanoparticles in Food Packaging and Coating Technologies: A Review.Biomolecules. 2023 Jul 7;13(7):1092. doi: 10.3390/biom13071092. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37509128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nettle-Leaf Extract Derived ZnO/CuO Nanoparticle-Biopolymer-Based Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Nanocomposite Packaging Films and Their Impact on Extending the Post-Harvest Shelf Life of Guava Fruit.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 5;11(2):224. doi: 10.3390/biom11020224. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33562547 Free PMC article.
-
Metal-based nanoparticles, sensors, and their multifaceted application in food packaging.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Aug 26;19(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00996-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34446005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of polysaccharides-based nanomaterials in food preservation and extension of shelf-life of food products: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Dec 1;252:126381. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126381. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37595723 Review.
Cited by
-
Romanian Wild-Growing Chelidonium majus-An Emerging Approach to a Potential Antimicrobial Engineering Carrier System Based on AuNPs: In Vitro Investigation and Evaluation.Plants (Basel). 2024 Mar 5;13(5):734. doi: 10.3390/plants13050734. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475580 Free PMC article.
-
From Past to Present: Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) in Daily LifeSynthesis Mechanisms, Influencing Factors, Characterization, Toxicity, and Emerging Applications in Biomedicine, Nanoelectronics, and Materials Science.ACS Omega. 2025 Jul 30;10(31):33999-34087. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c03162. eCollection 2025 Aug 12. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40821590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Compounds in Food Packaging.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 27;24(3):2457. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032457. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethanol and NaCl-Induced Gold Nanoparticle Aggregation Toxicity toward DNA Investigated with a DNA/GCE Biosensor.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 24;23(7):3425. doi: 10.3390/s23073425. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37050486 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterials for Smart and Sustainable Food Packaging: Nano-Sensing Mechanisms, and Regulatory Perspectives.Foods. 2025 Jul 29;14(15):2657. doi: 10.3390/foods14152657. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40807593 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amani P., Gadde L.-E. Shelf life extension and food waste reduction. Proc. Food Syst. Dyn. 2015:7–14.
-
- Kiss E. Nanotechnology in Food Systems: A Review. Acta Aliment. 2020;49:460–474. doi: 10.1556/066.2020.49.4.12. - DOI
-
- Sahraei F., Ahari H., Kakoolaki S. Effect of Bacillus subtilis as a probiotic on protein, lipid content, and trypsin and chymotrypsin enzymes in rainbow trout biometry (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Aquac. Int. 2018;27:141–153. doi: 10.1007/s10499-018-0313-8. - DOI
-
- Bouwmeester H., Dekkers S., Noordam M., Hagens W., Bulder A., De Heer C., ten Voorde S., Wijnhoven S., Sips A. Health Impact of Nanotechnologies in Food Production. National Institute for Public Health and the Environment Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport; Wageningen, The Netherlands: 2007. RIKILT Report.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases