Stabilizing Halogen-Bonded Complex between Metallic Anion and Iodide
- PMID: 36432170
- PMCID: PMC9692347
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27228069
Stabilizing Halogen-Bonded Complex between Metallic Anion and Iodide
Abstract
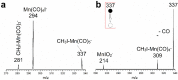
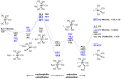
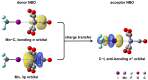
Halogen bonds (XBs) between metal anions and halides have seldom been reported because metal anions are reactive for XB donors. The pyramidal-shaped Mn(CO)5- anion is a candidate metallic XB acceptor with a ligand-protected metal core that maintains the negative charge and an open site to accept XB donors. Herein, Mn(CO)5- is prepared by electrospray ionization, and its reaction with CH3I in gas phase is studied using mass spectrometry and density functional theory (DFT) calculation. The product observed experimentally at m/z = 337 is assigned as [IMn(CO)4(OCCH3)]-, which is formed by successive nucleophilic substitution and reductive elimination, instead of the halogen-bonded complex (XC) CH3-I···Mn(CO)5-, because the I···Mn interaction is weak within XC and it could be a transient species. Inspiringly, DFT calculations predict that replacing CH3I with CF3I can strengthen the halogen bonding within the XC due to the electro-withdrawing ability of F. More importantly, in so doing, the nucleophilic substitution barrier can be raised significantly, ~30 kcal/mol, thus leaving the system trapping within the XC region. In brief, the combination of a passivating metal core and the introduction of an electro-withdrawing group to the halide can enable strong halogen bonding between metallic anion and iodide.
Keywords: halogen bond; metallic anion; nucleophilic substitution reaction; quantum chemistry calculation; reductive elimination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Designer Metallic Acceptor-Containing Halogen Bonds: General Strategies.Chemistry. 2017 Apr 24;23(23):5439-5442. doi: 10.1002/chem.201701067. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Chemistry. 2017. PMID: 28295738
-
"Anti-Electrostatic" Halogen Bonding.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Jun 26;59(27):11150-11157. doi: 10.1002/anie.202003083. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 32227661 Free PMC article.
-
The intramolecular hydrogen bonded-halogen bond: a new strategy for preorganization and enhanced binding.Chem Sci. 2018 Jun 21;9(26):5828-5836. doi: 10.1039/c8sc01973h. eCollection 2018 Jul 14. Chem Sci. 2018. PMID: 30079195 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen Bond Enhanced Halogen Bonds: A Synergistic Interaction in Chemistry and Biochemistry.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Oct 15;52(10):2870-2880. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00189. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31318520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strong N-X⋅⋅⋅O-N Halogen Bonds: A Comprehensive Study on N-Halosaccharin Pyridine N-Oxide Complexes.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Dec 16;58(51):18610-18618. doi: 10.1002/anie.201909759. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31613414 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

