Improved Activity of Herbal Medicines through Nanotechnology
- PMID: 36432358
- PMCID: PMC9695685
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12224073
Improved Activity of Herbal Medicines through Nanotechnology
Abstract
Phytochemicals or secondary metabolites are substances produced by plants that have been shown to have many biological activities, providing a scientific basis for using herbs in traditional medicine. In addition, the use of herbs is considered to be safe and more economical compared to synthetic medicine. However, herbal medicines have disadvantages, such as having low solubility, stability, and bioavailability. Some of them can undergo physical and chemical degradation, which reduces their pharmacological activity. In recent decades, nanotechnology-based herbal drug formulations have attracted attention due to their enhanced activity and potential for overcoming the problems associated with herbal medicine. Approaches using nanotechnology-based delivery systems that are biocompatible, biodegradable, and based on lipids, polymers, or nanoemulsions can increase the solubility, stability, bioavailability, and pharmacological activity of herbals. This review article aims to provide an overview of the latest advances in the development of nanotechnology-based herbal drug formulations for increased activity, as well as a summary of the challenges these delivery systems for herbal medicines face.
Keywords: bioactivity; drug delivery; herbal medicine; nanotechnology; phytochemical.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
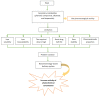
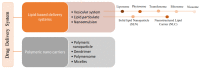

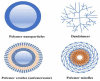
References
-
- Enrico C. Studies in Natural Products Chemistry. Volume 62 Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery of Natural Compounds and Phytochemicals for the Treatment of Cancer and Other Diseases.
-
- Martins-Gomes C., Souto E.B., Silva A.M. Systems of Nanovesicular Drug Delivery. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2022. Nanophytosomes: A Novel Approach for the Delivery of Herbal Drugs; pp. 239–257.
-
- Hussein R.A., El-Anssary A.A. Herbal Medicine. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2019. Plants Secondary Metabolites: The Key Drivers of the Pharmacological Actions of Medicinal Plants.
-
- Mendoza N., Silva E.M.E. Phytochemicals-Source of Antioxidants and Role in Disease Prevention. InTech; London, UK: 2018. Introduction to Phytochemicals: Secondary Metabolites from Plants with Active Principles for Pharmacological Importance.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

