Effects of Diet and Lifestyle on Audio-Vestibular Dysfunction in the Elderly: A Literature Review
- PMID: 36432406
- PMCID: PMC9698578
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14224720
Effects of Diet and Lifestyle on Audio-Vestibular Dysfunction in the Elderly: A Literature Review
Abstract
Background: The world's age-related health concerns continue to rise. Audio-vestibular disorders, such as hearing loss, tinnitus, and vertigo, are common complaints in the elderly and are associated with social and public health burdens. Various preventative measures can ease their impact, including healthy food consumption, nutritional supplementation, and lifestyle modification. We aim to provide a comprehensive summary of current possible strategies for preventing the age-related audio-vestibular dysfunction.
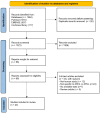
Methods: A PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane review databases search was conducted to identify the relationship between diet, lifestyle, and audio-vestibular dysfunction. "Diet", "nutritional supplement", "lifestyle", "exercise", "physical activity", "tinnitus", "vertigo" and "age-related hearing loss" were used as keywords.
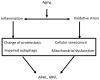
Results: Audio-vestibular dysfunction develops and progresses as a result of age-related inflammation and oxidative stress. Diets with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects have been proposed to alleviate this illness. A high-fat diet may induce oxidative stress and low protein intake is associated with hearing discomfort in the elderly. Increased carbohydrate and sugar intake positively correlate with the incidence of audio-vestibular dysfunction, whereas a Mediterranean-style diet can protect against the disease. Antioxidants in the form of vitamins A, C, and E; physical activity; good sleep quality; smoking cessation; moderate alcohol consumption; and avoiding noise exposure are also beneficial.
Conclusions: Adequate diet or nutritional interventions with lifestyle modification may protect against developing audio-vestibular dysfunction in elderly individuals.
Keywords: age-related hearing loss; audio-vestibular dysfunction; diet; lifestyle modification; nutritional intervention; tinnitus; vertigo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drugs inducing hearing loss, tinnitus, dizziness and vertigo: an updated guide.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Aug;24(15):7946-7952. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202008_22477. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32767320
-
Audio-vestibular signs and symptoms in Chiari malformation type i. Case series and literature review.Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2015 Jan-Feb;66(1):28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.otorri.2014.05.002. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2015. PMID: 25195076 Review. English, Spanish.
-
Does coronavirus affect the audio-vestibular system? A rapid systematic review.Int J Audiol. 2020 Jul;59(7):487-491. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2020.1776406. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Int J Audiol. 2020. PMID: 32530326
-
The possible effect of human menopausal gonadotropin on the audio-vestibular system.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2018 Dec;45(6):1166-1172. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2018.04.007. Epub 2018 May 7. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2018. PMID: 29747963
-
SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) and audio-vestibular disorders.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2021 Jan-Dec;35:20587384211027373. doi: 10.1177/20587384211027373. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34142589 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Plastic Events of the Vestibular Nucleus: the Initiation of Central Vestibular Compensation.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Nov;61(11):9680-9693. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04208-2. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38689145 Review.
-
Hearing and Diet (Narrative Review).Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Feb;76(1):1447-1453. doi: 10.1007/s12070-023-04238-7. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024. PMID: 38440452 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Hearing Loss and Eating Habits in the Older Population.Am J Lifestyle Med. 2023 Dec 1;19(3):361-367. doi: 10.1177/15598276231216392. eCollection 2025 Mar-Apr. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2023. PMID: 40041310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of 15 common dietary factors with tinnitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.BMJ Open. 2025 Mar 18;15(3):e091507. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-091507. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40101973 Free PMC article.
-
Association of oxidative balance score with hearing loss and tinnitus: NHANES 1999-2018.Front Nutr. 2024 Jun 19;11:1421605. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1421605. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38962438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Ageing and Health. [(accessed on 4 October 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health.
-
- Rechel B., Jagger C., McKee M., Cylus J., Normand C., Figueras J., North J., White C., editors. Living Longer, but in Better or Worse Health? European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies; Copenhagen, Denmark: 2020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

