Long-Term Effectiveness of a Smartphone App and a Smart Band on Arterial Stiffness and Central Hemodynamic Parameters in a Population with Overweight and Obesity (Evident 3 Study): Randomised Controlled Trial
- PMID: 36432446
- PMCID: PMC9695348
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14224758
Long-Term Effectiveness of a Smartphone App and a Smart Band on Arterial Stiffness and Central Hemodynamic Parameters in a Population with Overweight and Obesity (Evident 3 Study): Randomised Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: mHealth technologies could help to improve cardiovascular health; however, their effect on arterial stiffness and hemodynamic parameters has not been explored to date.
Objective: To evaluate the effect of a mHealth intervention, at 3 and 12 months, on arterial stiffness and central hemodynamic parameters in a sedentary population with overweight and obesity.
Methods: Randomised controlled clinical trial (Evident 3 study). 253 subjects were included: 127 in the intervention group (IG) and 126 in the control group (CG). The IG subjects were briefed on the use of the Evident 3 app and a smart band (Mi Band 2, Xiaomi) for 3 months to promote healthy lifestyles. All measurements were recorded in the baseline visit and at 3 and 12 months. The carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV) and the central hemodynamic parameters were measured using a SphigmoCor System® device, whereas the brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) and the Cardio Ankle Vascular Index (CAVI) were measured using a VaSera VS-2000® device.
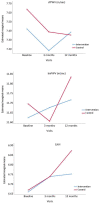
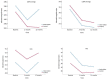
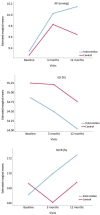
Results: Of the 253 subjects who attended the initial visit, 237 (93.7%) completed the visit at 3 months of the intervention, and 217 (85.3%) completed the visit at 12 months of the intervention. At 12 months, IG showed a decrease in peripheral augmentation index (PAIx) (-3.60; 95% CI -7.22 to -0.00) and ejection duration (ED) (-0.82; 95% CI -1.36 to -0.27), and an increase in subendocardial viability ratio (SEVR) (5.31; 95% CI 1.18 to 9.44). In CG, cfPWV decreased at 3 months (-0.28 m/s; 95% CI -0.54 to -0.02) and at 12 months (-0.30 m/s, 95% CI -0.54 to -0.05), central diastolic pressure (cDBP) decreased at 12 months (-1.64 mm/Hg; 95% CI -3.19 to -0.10). When comparing the groups we found no differences between any variables analyzed.
Conclusions: In sedentary adults with overweight or obesity, the multicomponent intervention (Smartphone app and an activity-tracking band) for 3 months did not modify arterial stiffness or the central hemodynamic parameters, with respect to the control group. However, at 12 months, CG presented a decrease of cfPWV and cDBP, whereas IG showed a decrease of PAIx and ED and an increase of SEVR.
Keywords: arterial stiffness; central hemodynamic parameters; eHealth; mobile app; mobile phone; telemedicine; weight control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stenholm S., Head J., Kivimäki M., Kawachi I., Aalto V., Zins M., Goldberg M., Zaninotto P., Magnuson Hanson L., Westerlund H., et al. Smoking, physical inactivity and obesity as predictors of healthy and disease-free life expectancy between ages 50 and 75: A multicohort study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016;45:1260–1270. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyw126. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baillot A., Romain A.J., Boisvert-Vigneault K., Audet M., Baillargeon J.P., Dionne I.J., Valiquette L., Chakra C.N., Avignon A., Langlois M.F. Effects of lifestyle interventions that include a physical activity component in class II and III obese individuals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0119017. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Acosta A., Streett S., Kroh M.D., Cheskin L.J., Saunders K.H., Kurian M., Schofield M., Barlow S.E., Aronne L. White Paper AGA: POWER—Practice Guide on Obesity and Weight Management, Education, and Resources. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017;15:631–649.e610. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.10.023. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

