Bioinspired Electropun Fibrous Materials Based on Poly-3-Hydroxybutyrate and Hemin: Preparation, Physicochemical Properties, and Weathering
- PMID: 36433006
- PMCID: PMC9692885
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14224878
Bioinspired Electropun Fibrous Materials Based on Poly-3-Hydroxybutyrate and Hemin: Preparation, Physicochemical Properties, and Weathering
Abstract
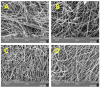
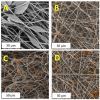
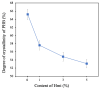
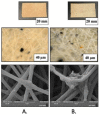
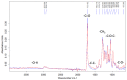
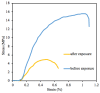
The development of innovative fibrous materials with valuable multifunctional properties based on biodegradable polymers and modifying additives presents a challenging direction for modern materials science and environmental safety. In this work, high-performance composite fibrous materials based on semicrystalline biodegradable poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) and natural iron-containing porphyrin, hemin (Hmi) were prepared by electrospinning. The addition of Hmi to the feed PHB mixture (at concentrations above 3 wt.%) is shown to facilitate the electrospinning process and improve the quality of the electrospun PHB/Hmi materials: the fibers become uniform, their average diameter decreases down to 1.77 µm, and porosity increases to 94%. Structural morphology, phase composition, and physicochemical properties of the Hmi/PHB fibrous materials were studied by diverse physicochemical methods, including electronic paramagnetic resonance, optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, elemental analysis, differential scanning calorimetry, Fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy, mechanical analysis, etc. The proposed nonwoven Hmi/PHB composites with high porosity, good mechanical properties, and retarded biodegradation due to high antibacterial potential can be used as high-performance and robust materials for biomedical applications, including breathable materials for wound disinfection and accelerated healing, scaffolds for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
Keywords: biodegradable polymers; electrospinning; hemin; new technologies; outdoor weathering; poly(3-hydroxybutyrate).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Structure and Performance of All-Green Electrospun PHB-Based Membrane Fibrous Biomaterials Modified with Hemin.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Apr 28;13(5):478. doi: 10.3390/membranes13050478. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37233539 Free PMC article.
-
Life Cycle of Functional All-Green Biocompatible Fibrous Materials Based on Biodegradable Polyhydroxybutyrate and Hemin: Synthesis, Service Life, and the End-of-Life via Biodegradation.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024 Apr 15;7(4):2325-2337. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.4c00010. Epub 2024 Mar 14. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024. PMID: 38483087
-
The Comparison of Advanced Electrospun Materials Based on Poly(-3-hydroxybutyrate) with Natural and Synthetic Additives.J Funct Biomater. 2022 Feb 28;13(1):23. doi: 10.3390/jfb13010023. J Funct Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35323223 Free PMC article.
-
Modified poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-based scaffolds in tissue engineering applications: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jan 1;166:986-998. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.255. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33152357 Review.
-
Polyhydroxybutyrate blends: A solution for biodegradable packaging?Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 May 15;207:263-277. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.02.185. Epub 2022 Mar 5. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 35257732 Review.
Cited by
-
Biocompatibility and Antimicrobial Activity of Electrospun Fibrous Materials Based on PHB and Modified with Hemin.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Jan 5;13(2):236. doi: 10.3390/nano13020236. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36677989 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and Performance of All-Green Electrospun PHB-Based Membrane Fibrous Biomaterials Modified with Hemin.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Apr 28;13(5):478. doi: 10.3390/membranes13050478. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37233539 Free PMC article.
-
Porphyrin-based electrospun nanomaterials for life science applications.BBA Adv. 2025 Apr 16;7:100160. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2025.100160. eCollection 2025. BBA Adv. 2025. PMID: 40337086 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic Materials Based on Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate and Chlorophyll Derivatives.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Dec 28;16(1):101. doi: 10.3390/polym16010101. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201766 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Poltronieri P., Kumar P. Handbook of Ecomaterials. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2017. Polyhydroxyalcanoates (PHAs) in Industrial Applications; pp. 1–30. - DOI
-
- Rajan K.P., Thomas S.P., Gopanna A., Chavali M. Handbook of Ecomaterials. Springer International Publishing AG; Cham, Switzerland: 2017. Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB): A Standout Biopolymer for Environmental Sustainability; pp. 1–23. - DOI
-
- Moydeen M.A., Syed A.M., Padusha E.F., Aboelfetoh S.S., Al-Deyab M.H. Fabrication of electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/dextran nanofibers via emulsion process as drug delivery system: Kinetics and in vitro release study. Int. J. of Biol. Macromol. 2018;116:1250–1259. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.130. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

