The Alterations and Roles of Glycosaminoglycans in Human Diseases
- PMID: 36433141
- PMCID: PMC9694910
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14225014
The Alterations and Roles of Glycosaminoglycans in Human Diseases
Abstract
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are a heterogeneous family of linear polysaccharides which are composed of a repeating disaccharide unit. They are also linked to core proteins to form proteoglycans (PGs). GAGs/PGs are major components of the cell surface and the extracellular matrix (ECM), and they display critical roles in development, normal function, and damage response in the body. Some properties (such as expression quantity, molecular weight, and sulfation pattern) of GAGs may be altered under pathological conditions. Due to the close connection between these properties and the function of GAGs/PGs, the alterations are often associated with enormous changes in the physiological/pathological status of cells and organs. Therefore, these GAGs/PGs may serve as marker molecules of disease. This review aimed to investigate the structural alterations and roles of GAGs/PGs in a range of diseases, such as atherosclerosis, cancer, diabetes, neurodegenerative disease, and virus infection. It is hoped to provide a reference for disease diagnosis, monitoring, prognosis, and drug development.
Keywords: ECM remodeling; chondroitin sulfate; dermatan sulfate; glycosaminoglycan; heparan sulfate; human disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

 ” and “
” and “ ” indicate that the hydroxyl can be substituted by a sulfate group and acetyl, respectively. It is worth noting that the structural formula represents the maximum degree of sulfation for each GAG type. “
” indicate that the hydroxyl can be substituted by a sulfate group and acetyl, respectively. It is worth noting that the structural formula represents the maximum degree of sulfation for each GAG type. “ ” only represents the possibility of being substituted by a sulfate group. Such as CS, they can be classified as CS-A (GlcA-GalNAc4S), CS-C (GlcA-GalNAc6S), CS-D (GlcA2S-GalNAc6S), CS-E (GlcA4S-GalNAc6S), etc. (Used with permission of Royal Society of Chemistry from ref. [1]; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc).
” only represents the possibility of being substituted by a sulfate group. Such as CS, they can be classified as CS-A (GlcA-GalNAc4S), CS-C (GlcA-GalNAc6S), CS-D (GlcA2S-GalNAc6S), CS-E (GlcA4S-GalNAc6S), etc. (Used with permission of Royal Society of Chemistry from ref. [1]; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc).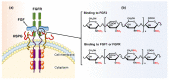
Similar articles
-
Matrix glycosaminoglycans in the growth phase of fibroblasts: more of the story in wound healing.J Surg Res. 2000 Jul;92(1):45-52. doi: 10.1006/jsre.2000.5840. J Surg Res. 2000. PMID: 10864481
-
Disease-specific glycosaminoglycan patterns in the extracellular matrix of human lung and brain.Carbohydr Res. 2022 Jan;511:108480. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2021.108480. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Carbohydr Res. 2022. PMID: 34837849 Review.
-
"GAG-ing with the neuron": The role of glycosaminoglycan patterning in the central nervous system.Exp Neurol. 2015 Dec;274(Pt B):100-14. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.08.004. Epub 2015 Aug 12. Exp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26277685 Review.
-
Role of proteoglycans in cell adhesion of prostate cancer cells: from review to experiment.Urol Res. 1997;25 Suppl 2:S89-96. doi: 10.1007/BF00941994. Urol Res. 1997. PMID: 9144893
-
Glycosaminoglycans, Instructive Biomolecules That Regulate Cellular Activity and Synaptic Neuronal Control of Specific Tissue Functional Properties.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 12;26(6):2554. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062554. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141196 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteoglycan Dysfunction: A Common Link Between Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Skeletal Dysplasia.Neurospine. 2024 Mar;21(1):162-178. doi: 10.14245/ns.2347342.671. Epub 2024 Mar 31. Neurospine. 2024. PMID: 38569642 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in the Molecular and Biochemical Mechanisms of Cervical Ripening: A Comprehensive Review.Cells. 2024 Mar 29;13(7):600. doi: 10.3390/cells13070600. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38607039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the Impact of Mechanical Properties and Cell-Collagen Interaction on NIH3T3 Function: A Comparative Study on Different Substrates and Culture Environments.Gels. 2023 Nov 22;9(12):922. doi: 10.3390/gels9120922. Gels. 2023. PMID: 38131908 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial polysaccharide lyase family 33: Specificity from an evolutionarily conserved binding tunnel.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Feb 18;122(7):e2421623122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2421623122. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 39932998 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogens that infect mammalian cells via sulfonated glycosaminoglycans.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 10;15:1613923. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1613923. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40557318 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

