Microbial pyrazine diamine is a novel electrolyte additive that shields high-voltage LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 cathodes
- PMID: 36434117
- PMCID: PMC9700740
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-22018-1
Microbial pyrazine diamine is a novel electrolyte additive that shields high-voltage LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 cathodes
Abstract
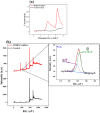
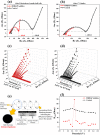
The uncontrolled oxidative decomposition of electrolyte while operating at high potential (> 4.2 V vs Li/Li+) severely affects the performance of high-energy density transition metal oxide-based materials as cathodes in Li-ion batteries. To restrict this degradative response of electrolyte species, the need for functional molecules as electrolyte additives that can restrict the electrolytic decomposition is imminent. In this regard, bio-derived molecules are cost-effective, environment friendly, and non-toxic alternatives to their synthetic counter parts. Here, we report the application of microbially synthesized 2,5-dimethyl-3,6-bis(4-aminobenzyl)pyrazine (DMBAP) as an electrolyte additive that stabilizes high-voltage (4.5 V vs Li/Li+) LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2 cathodes. The high-lying highest occupied molecular orbital of bio-additive (DMBAP) inspires its sacrificial in situ oxidative decomposition to form an organic passivation layer on the cathode surface. This restricts the excessive electrolyte decomposition to form a tailored cathode electrolyte interface to administer cyclic stability and enhance the capacity retention of the cathode.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Scrosati B, Hassoun J, Sun Y-K. Lithium-ion batteries. A look into the future. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011;4:3287–3295. doi: 10.1039/c1ee01388b. - DOI
-
- Weiss M, et al. Fast charging of lithium-ion batteries: A review of materials aspects. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021;11:2101126. doi: 10.1002/aenm.202101126. - DOI
-
- Yan J, Liu X, Li B. Recent progress in Li-rich layered oxides as cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2014;4:63268–63284. doi: 10.1039/C4RA12454E. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

