Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the SPL transcription factor family and its response to abiotic stress in Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa)
- PMID: 36434504
- PMCID: PMC9701020
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-022-08977-9
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the SPL transcription factor family and its response to abiotic stress in Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa)
Abstract
Background: Squamous promoter binding protein-like (SPL) proteins are a class of transcription factors that play essential roles in plant growth and development, signal transduction, and responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. The rapid development of whole genome sequencing has enabled the identification and characterization of SPL gene families in many plant species, but to date this has not been performed in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa).
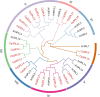
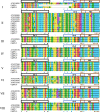
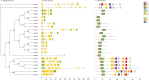
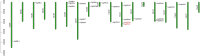
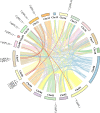
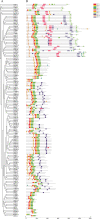
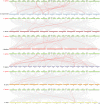
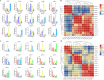
Results: This study identified 23 SPL genes in quinoa, which were unevenly distributed on 18 quinoa chromosomes. Quinoa SPL genes were then classified into eight subfamilies based on homology to Arabidopsis thaliana SPL genes. We selected three dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous representative species, each associated with C. quinoa, for comparative sympatric mapping to better understand the evolution of the developmental mechanisms of the CqSPL family. Furthermore, we also used 15 representative genes from eight subfamilies to characterize CqSPLs gene expression in different tissues and at different fruit developmental stages under six different abiotic stress conditions.
Conclusions: This study, the first to identify and characterize SPL genes in quinoa, reported that CqSPL genes, especially CqSPL1, play a critical role in quinoa development and in its response to various abiotic stresses.
Keywords: Abiotic stress; Chenopodium quinoa; Genome-wide analysis; SPL gene family.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of SPL Family Genes in Chenopodium quinoa.Genes (Basel). 2022 Aug 16;13(8):1455. doi: 10.3390/genes13081455. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011366 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic analysis, and expression profiles of trihelix transcription factor family genes in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) under abiotic stress conditions.BMC Genomics. 2022 Jul 10;23(1):499. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08726-y. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35810309 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and expression analysis of the CqSnRK2 gene family and a functional study of the CqSnRK2.12 gene in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.).BMC Genomics. 2022 May 24;23(1):397. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08626-1. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35610576 Free PMC article.
-
Progress on genomics and locus of important agronomic traits in Chenopodium quinoa.Yi Chuan. 2022 Nov 20;44(11):1009-1027. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-289. Yi Chuan. 2022. PMID: 36384994 Review.
-
Quinoa Abiotic Stress Responses: A Review.Plants (Basel). 2018 Nov 29;7(4):106. doi: 10.3390/plants7040106. Plants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30501077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of YABBY Genes in Chenopodium quinoa.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 19;14(11):2103. doi: 10.3390/genes14112103. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38003046 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of the SPL transcription factor family and its response to water stress in sunflower (Helianthus annuus).Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 Nov;28(6):943-958. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01388-z. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023. PMID: 37938528 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the SPL transcription factor family and its response to abiotic stress in Pisum sativum L.BMC Genomics. 2024 May 31;25(1):539. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10262-w. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38822248 Free PMC article.
-
Genome assembly of a diversity panel of Chenopodium quinoa.Sci Data. 2024 Dec 18;11(1):1366. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-04200-4. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 39695301 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Ginkgo biloba SPL Gene Family and Expression Analysis in Flavonoid Biosynthesis and Water Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 21;26(10):4932. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104932. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40430070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yasui Y, Hirakawa H, Oikawa T, Toyoshima M, Matsuzaki C, Ueno M, Mizuno N, Nagatoshi Y, Imamura T, Miyago M. Draft genome sequence of an inbred line of Chenopodium quinoa, an allotetraploid crop with great environmental adaptability and outstanding nutritional properties. DNA Res. 2016;23(6):535–546. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsw037. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zurita-Silva A, Fuentes F, Zamora P, Jacobsen S, Schwember AR. Breeding quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) potential and perspectives. Mol Breeding. 2014;34(1):13–30. doi: 10.1007/s11032-014-0023-5. - DOI
-
- Schmöckel SM, Lightfoot DJ, Razali R, Tester M, Jarvis DE. Identification of putative transmembrane proteins involved in salinity tolerance in Chenopodium quinoa by integrating physiological data, RNAseq, and SNP analyses. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:1023–1046. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

