Changes in women's physical function in mid-life by reproductive age and hormones: a longitudinal study
- PMID: 36434722
- PMCID: PMC9700972
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-022-02070-9
Changes in women's physical function in mid-life by reproductive age and hormones: a longitudinal study
Abstract
Background: Whether women's physical function in mid-life is related to their reproductive age is not known. The objectives of this study were to examine and compare changes in physical function in women by reproductive age, measured as time since final menstrual period (FMP), and chronological age, and to explore associations with repeatedly assessed levels of reproductive hormones.
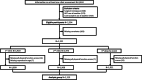
Methods: We used data from 2319 UK women with up to three repeated measurements of physical function (median length of follow up: 2 years), focusing on changes occurring in women experiencing a natural menopausal transition. The main outcome was a composite physical function score that incorporated assessments of strength (grip strength), balance (one-leg stand) and cardiorespiratory fitness (timed chair rises). Associations with time since FMP, age, and time-updated measures of anti-Müllerian hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone were assessed by multilevel models and generalised estimating equations models adjusted for the underlying effects of chronological age and confounding by education, age at first birth and smoking.
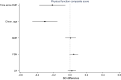
Results: The results showed that, adjusted for these confounders, time since FMP (- 0.21 SD per 10 years, 95% CI - 0.37, - 0.06) and chronological age (- 0.31 SD per 10 years, 95% CI - 0.46, - 0.15) were inversely associated with the physical function composite score. Grip strength seemed to be the main contributor to the decline in the composite score by time since FMP. There was no strong evidence of associations between any of the three reproductive hormones and the composite score.
Conclusions: Physical function in women in mid-life declined with both chronological and reproductive age. The decline with reproductive age was independent of chronological age but did not seem to be driven by changes in reproductive hormones.
Keywords: ALSPAC; Menopause; Physical function; Reproductive age; Reproductive hormones.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AF and KT report funding from UK MRC, DAL reports receiving support from several national and international government and charity research funders, and Grants from Medtronic Ltd for work unrelated to that presented here. SMN reports personal fees from Access Fertility, personal fees from Merck, personal fees from Ferring, Grants and personal fees from Roche Diagnostics, personal fees from The Fertility Partnership and personal fees from Modern Fertility, outside the submitted work. Roche Diagnostics provided support in kind for the hormone assays used in this report, and have not contributed to the statistical analysis plan, analysis of data, interpretation of results or any part of the manuscript. PW declares Grant funding from Roche Diagnostics, Astrazeneca, and Boheringer Ingelheim. FK, ALGS, GLC, NS declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Guralnik JM, Ferrucci L, Pieper CF, Leveille SG, Markides KS, Ostir GV, et al. Lower extremity function and subsequent disability: Consistency across studies, predictive models, and value of gait speed alone compared with the short physical performance battery. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2000;55:M221–M231. doi: 10.1093/gerona/55.4.M221. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

