Integrated metabolomics, network pharmacology and biological verification to reveal the mechanisms of Nauclea officinalis treatment of LPS-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 36434729
- PMCID: PMC9700915
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-022-00685-6
Integrated metabolomics, network pharmacology and biological verification to reveal the mechanisms of Nauclea officinalis treatment of LPS-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
Background: Acute lung injury (ALI) is a severe inflammatory disease, underscoring the urgent need for novel treatments. Nauclea officinalis Pierre ex Pitard (Danmu in Chinese, DM) is effective in treating inflammatory respiratory diseases. However, there is still no evidence of its protective effect against ALI.
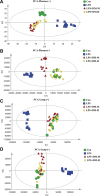
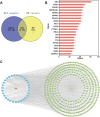
Methods: Metabolomics was applied to identify the potential biomarkers and pathways in ALI treated with DM. Further, network pharmacology was introduced to predict the key targets of DM against ALI. Then, the potential pathways and key targets were further verified by immunohistochemistry and western blot assays.
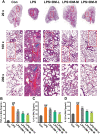
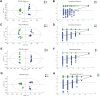
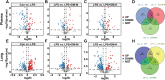
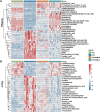
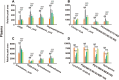
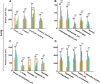
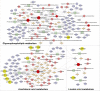
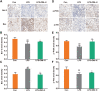
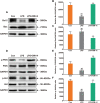
Results: DM significantly improved lung histopathological characteristics and inflammatory response in LPS-induced ALI. Metabolomics analysis showed that 16 and 19 differential metabolites were identified in plasma and lung tissue, respectively, and most of these metabolites tended to recover after DM treatment. Network pharmacology analysis revealed that the PI3K/Akt pathway may be the main signaling pathway of DM against ALI. The integrated analysis of metabolomics and network pharmacology identified 10 key genes. These genes are closely related to inflammatory response and cell apoptosis of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI in mice. Furthermore, immunohistochemistry and western blot verified that DM could regulate inflammatory response and cell apoptosis by affecting the PI3K/Akt pathway, and expression changes in Bax and Bcl-2 were also triggered.
Conclusion: This study first integrated metabolomics, network pharmacology and biological verification to investigate the potential mechanism of DM in treating ALI, which is related to the regulation of inflammatory response and cell apoptosis. And the integrated analysis can provide new strategies and ideas for the study of traditional Chinese medicines in the treatment of ALI.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Mechanisms; Metabolomics; Nauclea officinalis; Network pharmacology.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Systems pharmacology reveals the mechanism of activity of Ge-Gen-Qin-Lian decoction against LPS-induced acute lung injury: A novel strategy for exploring active components and effective mechanism of TCM formulae.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Jun;156:104759. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104759. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32200026
-
Uncovering the active constituents and mechanisms of Rujin Jiedu powder for ameliorating LPS-induced acute lung injury using network pharmacology and experimental investigations.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 11;14:1186699. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1186699. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37251341 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the effective components and underlying mechanisms of Feiyanning formula in acute lung injury based on the pharmacokinetics, metabolomics and network pharmacology technology.Fitoterapia. 2025 Jun;183:106486. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2025.106486. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Fitoterapia. 2025. PMID: 40120984
-
Integrated network pharmacology and experimental validation-based approach to reveal the underlying mechanisms and key material basis of Jinhua Qinggan granules against acute lung injury.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 May 23;326:117920. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117920. Epub 2024 Feb 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38373663
-
Network Pharmacology Studies on the Bioactive Compounds and Action Mechanisms of Natural Products for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: A Review.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Feb 23;8:74. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00074. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28280467 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Saiga antelope horn suppresses febrile seizures in rats by regulating neurotransmitters and the arachidonic acid pathway.Chin Med. 2024 Jun 3;19(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00949-3. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38831318 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology: a bright guiding light on the way to explore the personalized precise medication of traditional Chinese medicine.Chin Med. 2023 Nov 8;18(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00853-2. Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 37941061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effects of Danmu Extract Syrup on Acute Lung Injury Induced by Lipopolysaccharide in Mice through Endothelial Barrier Repair.Chin J Integr Med. 2024 Mar;30(3):243-250. doi: 10.1007/s11655-023-3604-5. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Chin J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 37987961
-
Analysis of the Protective Effects of Rosa roxburghii-Fermented Juice on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice through Network Pharmacology and Metabolomics.Nutrients. 2024 Apr 30;16(9):1376. doi: 10.3390/nu16091376. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38732622 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways and potential therapeutic targets in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).Respir Res. 2024 Jan 13;25(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02678-5. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38218783 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

