Bacterial resistance to antibacterial agents: Mechanisms, control strategies, and implications for global health
- PMID: 36435256
- PMCID: PMC11537282
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160461
Bacterial resistance to antibacterial agents: Mechanisms, control strategies, and implications for global health
Abstract
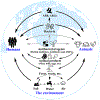
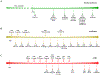
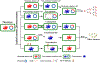
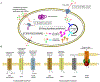
The spread of bacterial drug resistance has posed a severe threat to public health globally. Here, we cover bacterial resistance to current antibacterial drugs, including traditional herbal medicines, conventional antibiotics, and antimicrobial peptides. We summarize the influence of bacterial drug resistance on global health and its economic burden while highlighting the resistance mechanisms developed by bacteria. Based on the One Health concept, we propose 4A strategies to combat bacterial resistance, including prudent Application of antibacterial agents, Administration, Assays, and Alternatives to antibiotics. Finally, we identify several opportunities and unsolved questions warranting future exploration for combating bacterial resistance, such as predicting genetic bacterial resistance through the use of more effective techniques, surveying both genetic determinants of bacterial resistance and the transmission dynamics of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs).
Keywords: Antibiotics; Antimicrobial peptides; Bacterial resistance; Global health; Mechanism of action; Strategies.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Cesar de la Fuente-Nunez provides consulting services to Invaio Sciences and is a member of the Scientific Advisory Boards of Nowture S.L. and Phare Bio. The de la Fuente Lab has received research funding or in-kind donations from United Therapeutics, Strata Manufacturing PJSC, and Procter & Gamble, none of which were used in support of this work. All other authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this review.
Figures
References
-
- Abdallah A, Zhang P, Zhong Q, et al., 2019. Application of traditional Chinese herbal medicine by-products as dietary feed supplements and antibiotic replacements in animal production. Curr. Drug Metab 20, 54–64. - PubMed
-
- Abdi M, Mirkalantari S, Amirmozafari N, 2019. Bacterial resistance to antimicrobial peptides. J. Pept. Sci 25, e3210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

