Elevated TGFβ signaling contributes to cerebral small vessel disease in mouse models of Gould syndrome
- PMID: 36435425
- PMCID: PMC10393528
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2022.11.007
Elevated TGFβ signaling contributes to cerebral small vessel disease in mouse models of Gould syndrome
Abstract
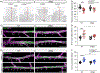
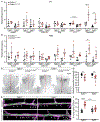
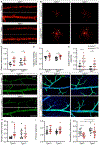
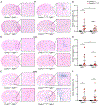
Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) is a leading cause of stroke and vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Studying monogenic CSVD can reveal pathways that are dysregulated in common sporadic forms of the disease and may represent therapeutic targets. Mutations in collagen type IV alpha 1 (COL4A1) and alpha 2 (COL4A2) cause highly penetrant CSVD as part of a multisystem disorder referred to as Gould syndrome. COL4A1 and COL4A2 form heterotrimers [a1α1α2(IV)] that are fundamental constituents of basement membranes. However, their functions are poorly understood and the mechanism(s) by which COL4A1 and COL4A2 mutations cause CSVD are unknown. We used histological, molecular, genetic, pharmacological, and in vivo imaging approaches to characterize central nervous system (CNS) vascular pathologies in Col4a1 mutant mouse models of monogenic CSVD to provide insight into underlying pathogenic mechanisms. We describe developmental CNS angiogenesis abnormalities characterized by impaired retinal vascular outgrowth and patterning, increased numbers of mural cells with abnormal morphologies, altered contractile protein expression in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and age-related loss of arteriolar VSMCs in Col4a1 mutant mice. Importantly, we identified elevated TGFβ signaling as a pathogenic consequence of Col4a1 mutations and show that genetically suppressing TGFβ signaling ameliorated CNS vascular pathologies, including partial rescue of retinal vascular patterning defects, prevention of VSMC loss, and significant reduction of intracerebral hemorrhages in Col4a1 mutant mice aged up to 8 months. This study identifies a novel biological role for collagen α1α1α2(IV) as a regulator of TGFβ signaling and demonstrates that elevated TGFβ signaling contributes to CNS vascular pathologies caused by Col4a1 mutations. Our findings suggest that pharmacologically suppressing TGFβ signaling could reduce the severity of CSVD, and potentially other manifestations associated with Gould syndrome and have important translational implications that could extend to idiopathic forms of CSVD.
Keywords: Basement membrane; CSVD; Gould syndrome; TGFβ; Type IV collagen.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Collagen IV deficiency causes hypertrophic remodeling and endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization in small vessel disease with intracerebral hemorrhage.EBioMedicine. 2024 Sep;107:105315. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105315. Epub 2024 Aug 30. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39216230 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal pathology in mouse models of Gould syndrome is partially alleviated by genetically reducing TGFβ signaling.Matrix Biol. 2024 Nov;133:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2024.07.005. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Matrix Biol. 2024. PMID: 39097038 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated TGFβ signaling contributes to ocular anterior segment dysgenesis in Col4a1 mutant mice.Matrix Biol. 2022 Jun;110:151-173. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2022.05.001. Epub 2022 May 4. Matrix Biol. 2022. PMID: 35525525 Free PMC article.
-
Role of COL4A1 in basement-membrane integrity and cerebral small-vessel disease. The COL4A1 stroke syndrome.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(13):1317-24. doi: 10.2174/092986710790936293. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20166936 Review.
-
COL4A1 and COL4A2 mutations and disease: insights into pathogenic mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.Hum Mol Genet. 2012 Oct 15;21(R1):R97-110. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds346. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2012. PMID: 22914737 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired intracellular Ca2+ signaling contributes to age-related cerebral small vessel disease in Col4a1 mutant mice.Sci Signal. 2023 Nov 14;16(811):eadi3966. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.adi3966. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Sci Signal. 2023. PMID: 37963192 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular biomarkers for vascular cognitive impairment and dementia.Nat Rev Neurol. 2023 Dec;19(12):737-753. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00884-1. Epub 2023 Nov 13. Nat Rev Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37957261 Review.
-
PI3K block restores age-dependent neurovascular coupling defects associated with cerebral small vessel disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Aug 29;120(35):e2306479120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2306479120. Epub 2023 Aug 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37607233 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating neural crest cell migration in a Col4a1 mutant mouse model of ocular anterior segment dysgenesis.Cells Dev. 2024 Sep;179:203926. doi: 10.1016/j.cdev.2024.203926. Epub 2024 May 9. Cells Dev. 2024. PMID: 38729574 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in fibulin-1 and collagen IV suppress the short healthspan of mig-17/ADAMTS mutants in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 9;19(7):e0305396. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305396. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38980840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosetti F, Galis ZS, Bynoe MS, Charette M, Cipolla MJ, Del Zoppo GJ, Gould D, Hatsukami TS, Jones TL, Koenig JI, Lutty GA, Maric-Bilkan C, Stevens T, Tolunay HE, Koroshetz W and Small Blood Vessels: Big Health Problems” Workshop P. “Small Blood Vessels: Big Health Problems?”: Scientific Recommendations of the National Institutes of Health Workshop. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016;5. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

