Detrimental Effects of Alcohol-Induced Inflammation on Brain Health: From Neurogenesis to Neurodegeneration
- PMID: 36436159
- PMCID: PMC11412203
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-022-01308-2
Detrimental Effects of Alcohol-Induced Inflammation on Brain Health: From Neurogenesis to Neurodegeneration
Abstract
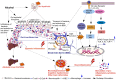
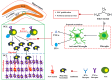
Alcohol consumption is known to cause several brain anomalies. The pathophysiological changes associated with alcohol intoxication are mediated by various factors, most notable being inflammation. Alcohol intoxication may cause inflammation through several molecular mechanisms in multiple organs, including the brain, liver and gut. Alcohol-induced inflammation in the brain and gut are intricately connected. In the gut, alcohol consumption leads to the weakening of the intestinal barrier, resulting in bacteria and bacterial endotoxins permeating into the bloodstream. These bacterial endotoxins can infiltrate other organs, including the brain, where they cause cognitive dysfunction and neuroinflammation. Alcohol can also directly affect the brain by activating immune cells such as microglia, triggering the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and neuroinflammation. Since alcohol causes the death of neural cells, it has been correlated to an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Besides, alcohol intoxication has also negatively affected neural stem cells, affecting adult neurogenesis and causing hippocampal dysfunctions. This review provides an overview of alcohol-induced brain anomalies and how inflammation plays a crucial mechanistic role in alcohol-associated pathophysiology.
Keywords: Adult neurogenesis; Alcohol intoxication; Neurodegeneration; Neuroinflammation; Toxicity.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahluwalia V, Wade JB, Moeller FG, White MB, Unser AB, Gavis EA, Sterling RK, Stravitz RT, Sanyal AJ, Siddiqui MS, Puri P, Luketic V, Heuman DM, Fuchs M, Matherly S, Bajaj JS (2015) The etiology of cirrhosis is a strong determinant of brain reserve: a multimodal magnetic resonance imaging study. Liver Transpl 21(9):1123–1132. 10.1002/lt.24163 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmad A, Shah SA, Badshah H, Kim MJ, Ali T, Yoon GH, Kim TH, Abid NB, Rehman SU, Khan S, Kim MO (2016) Neuroprotection by vitamin C against ethanol-induced neuroinflammation associated neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 15(3):360–370. 10.2174/1871527315666151110130139 - PubMed
-
- Akers KG, Martinez-Canabal A, Restivo L, Yiu AP, De Cristofaro A, Hsiang HL, Wheeler AL, Guskjolen A, Niibori Y, Shoji H, Ohira K, Richards BA, Miyakawa T, Josselyn SA, Frankland PW (2014) Hippocampal neurogenesis regulates forgetting during adulthood and infancy. Science 344(6184):598–602. 10.1126/science.1248903 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

