A prospective, single centre, open label, single arm pilot study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Amlapitta Mishran Suspension in participants with endoscopic gastritis
- PMID: 36436294
- PMCID: PMC9700308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaim.2022.100664
A prospective, single centre, open label, single arm pilot study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Amlapitta Mishran Suspension in participants with endoscopic gastritis
Abstract
Background: Endoscopic gastritis is associated with symptoms of gastritis, along with endoscopic findings. Amlapitta Mishran has multiple active components that act via various mechanisms in patients with gastritis symptoms. We planned to conduct this study to find out the efficacy and safety of Amlapitta Mishran in patients with endoscopic gastritis.
Objectives: To find out efficacy of Amlapitta Mishran in patient with endoscopic gastritis.
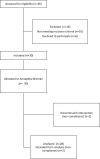
Materials and methods: This study was an open-label, prospective, single-center study. Thirty participants were recruited, and Amlapitta Mishran Suspension was given for 30 days. Blood investigations for safety were performed at baseline (Visit 1), on Visit 3 and Visit 4. Endoscopy was performed at baseline and Visit 4, and stomach erosion score was recorded. Amlapitta Symptom Rating Scale score, Postprandial Distress Syndrome (PPDS) score, and Epigastric Pain Syndrome (EPS) score were efficacy endpoints.
Results: Out of the 30 participants recruited, 28 participants completed the study. The median age of participants in the study was 26.50 years. A statistically significant (P<0.05) reduction was seen in endoscopy score at Visit 4 as compared to baseline (Visit 1) by Wilcoxon Signed Rank test. Amlapitta Symptom Rating Scale score, PPDS score, EPS score also exhibited significant reduction (P < 0.05) at Visit 3 and Visit 4 as compared to baseline by Friedman's test with post hoc analysis. No statistically significant reduction was seen in these scores from Visit 3 to Visit 4, except for the EPS score. At the end of Visit 4, 18 (64%) participants had an endoscopy score of 1 (no erosions). At the end of Visit 4, ≥ 50% improvement was seen in Amlapitta Symptom Rating Scale score in 27 (96%) participants, PPDS score improved by ≥ 50% in 25 (89%) participants, and EPS score improved by ≥ 50% in 26 (93%) participants. All safety variables including laboratory investigation were within the normal range in all visits.
Conclusion: Amlapitta Mishran Suspension effectively reduced endoscopic gastritis scores in the participants and reduced the symptoms of gastritis measured by the Amlapitta Symptom Rating Scale, PPDS, and EPS scores with no adverse events.
Keywords: Amlapitta; Ayurved; Gastritis; Gastroenterology.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest Nil.
References
-
- Chauhan G., Mahapatra A.K., Babar Kapoor A., Kumar A. Study on clinical efficacy of avipattikar choorna and sutasekhar rasa in the management of Urdhwaga Amlapitta. J Pharmaceut Sci Innovat. 2015;4:11–15. doi: 10.7897/2277-4572.0414. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources