Polysaccharide of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz alleviate lipopolysaccharide-stimulated liver inflammation injury of goslings through miR-223/NLRP3 axis
- PMID: 36436369
- PMCID: PMC9706645
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102285
Polysaccharide of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz alleviate lipopolysaccharide-stimulated liver inflammation injury of goslings through miR-223/NLRP3 axis
Abstract
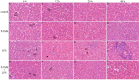
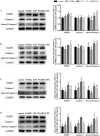
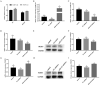
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) infection could cause severe liver inflammation and lead to liver damage, even death. Previous studies have shown that polysaccharide of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz (PAMK) could protect liver from inflammation caused by LPS in mice. However, whether PAMK could alleviate liver inflammatory injury in other animals with LPS is still unknown. For evaluating whether PAMK could alleviate liver inflammatory injury in goslings with LPS, a total of 80 healthy 1-day old Magang goslings were randomly divided into 4 groups (control group, PAMK group, LPS group, and PAMK+LPS group). Goslings in control group and LPS group were fed with basal diet, and goslings in PAMK group and PAMK+LPS group were fed basal diet supplemented with 400 mg/kg PAMK to the end of trial. On 24 d of age, goslings in the control group and PAMK group were intraperitoneal injected 0.5 mL normal saline, and goslings in LPS and PAMK+LPS groups were intraperitoneal injected with LPS at 5 mg/kg BW. The serum and liver samples were collected for further analysis after treatment of LPS at 6, 12, 24, and 48 h. Furthermore, the hepatocytes were extracted from goose embryo to measure the expression of the key genes of miR-223/NLRP3 axis. The results showed that PAMK pretreatment could maintain normal cell morphology of liver, alleviate the enhanced levels of biochemical indexes ALT and AST, decrease the levels of IL-1β and IL-18, increase the relative mRNA expression of miR-223, and decrease the expression of NLRP3, Caspase-1, and cleaved Caspase-1 in liver and hepatocytes of goslings induced by LPS. These results indicated that PAMK could relieve inflammatory liver tissue damage after LPS treatment and downregulate the level of inflammation factors via miR-223/NLRP3 axis, thus playing a liver protective role in liver inflammation injury in goslings.
Keywords: gosling; lipopolysaccharide; liver inflammation; miR-223/NLRP3 axis; polysaccharide of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
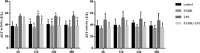
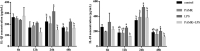
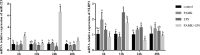
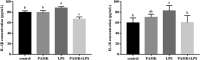
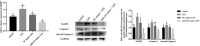
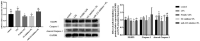
References
-
- Bauernfeind F., Rieger A., Schildberg F., Knolle P., Schmid-Burgk J., Hornung V. NLRP3 inflammasome activity is negatively controlled by miR-223. J. Immunol. 2012;189:4175–4181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

