Reduction of red blood spots in cooked marinated chicken breast meat by combined microwave heating and steaming
- PMID: 36436382
- PMCID: PMC9706636
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102317
Reduction of red blood spots in cooked marinated chicken breast meat by combined microwave heating and steaming
Abstract
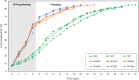
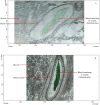
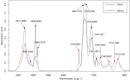
One of the defects commonly found in cooked marinated chicken breast products is a red blood spot (RBS), which is caused by undercooked blood in vessels. This problem was alleviated by microwave (MW) pre-heating for 6 to 7 min, followed by steaming. RBS formation decreased when samples were heated to a core temperature of 80°C and were completely eliminated at a core temperature of 82°C and 85°C when a MW pre-heating step was applied for 7 min. Based on synchrotron-based Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (SR-FTIR), blood remaining in the blood vessel had a lower α-helical content when samples were cooked by the combination of MW heating and steaming as compared with those prepared by steaming alone (P < 0.05). MW pre-heating decreased cooking time by 28 to 48% as compared with steaming alone. Heating regimes had no effect on cooking loss, pH, water-holding capacity, and shear force. MW pre-heating for 7 min followed by steaming to a core temperature of 82°C appeared to be an effective heating regime to reduce the occurrence of RBS, with acceptable cooking loss.
Keywords: blood denaturation; microwave heating; red blood spot; steaming; synchrotron radiation Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heating temperatures affect meat quality and vibrational spectroscopic properties of slow- and fast-growing chickens.Poult Sci. 2023 Aug;102(8):102754. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102754. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 37276701 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of marinating ingredients on temperature-induced denaturation of hemoglobin and its relation to red blood spot formation in cooked chicken breast.J Food Sci. 2020 Aug;85(8):2398-2405. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15308. Epub 2020 Jul 2. J Food Sci. 2020. PMID: 32614081
-
Dynamic changes of tenderness, moisture and protein in marinated chicken: the effect of different steaming temperatures.J Sci Food Agric. 2024 Sep;104(12):7668-7677. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13603. Epub 2024 May 20. J Sci Food Agric. 2024. PMID: 38767345
-
Contribution of collagen and connective tissue to cooked meat toughness; some paradigms reviewed.Meat Sci. 2018 Oct;144:127-134. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2018.03.026. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Meat Sci. 2018. PMID: 29636208 Review.
-
Influence of cooking techniques on food quality, digestibility, and health risks regarding lipid oxidation.Food Res Int. 2023 May;167:112685. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112685. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Food Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37087258 Review.
References
-
- Ali S.A., Lawson A.M., Tauson H.A., Jensen F.J., Chwalibog A. Influence of electrical stunning voltages on bleed out and carcass quality in slaughtered broiler chickens. Arch. Geflugelkd. 2007;71:35–40.
-
- AOAC . 18th ed. Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Washington, DC: 2010. Official Methods of Analysis.
-
- Awuah B.G., Ramaswamy S.H., Tang J. CRC. Press; New York, NY: 2015. Radio-Frequency Heating in Food Processing.
-
- Bertram C.H., Kohler A., Bocker U., Ofstad R., Andersen J.A. Heat-induced changes in myofibrillar protein structures and myowater of two pork qualities: A combined FT-IR spectroscopy and low-field NMR relaxometry study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006;54:1740–1746. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

