Transitional B cell cytokines risk stratify early borderline rejection after renal transplantation
- PMID: 36436679
- PMCID: PMC10038876
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.10.026
Transitional B cell cytokines risk stratify early borderline rejection after renal transplantation
Abstract
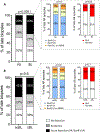
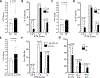
Borderline rejection (BL) in renal transplantation is associated with decreased allograft survival, yet many patients with BL maintain stable graft function. Identifying patients with early BL at risk for shortened allograft survival would allow for timely targeted therapeutic intervention aimed at improving outcomes. 851/1187 patients transplanted between 2013-18 underwent early biopsy (0-4 mos). 217/851 (25%) had BL and were compared to 387/851 without significant inflammation (NI). Serial surveillance and for-cause biopsies and seven-year follow-up were used to evaluate histological and clinical progression. To identify high-risk patients, we examined clinical/histological parameters using regression and non-linear dimensionality reduction (tSNE) and a biomarker based on peripheral blood transitional-1 B cell (T1B) IL-10/TNFα ratio. Compared to NI, early BL was associated with increased progression to late acute rejection (AR; 5-12 mos), premature interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IFTA) and decreased seven-year graft survival. However, decreased graft survival was limited to BL patients who progressed to late AR or IFTA, and was not influenced by treatment. Although tSNE clustered patients into groups based on clinical factors, the ability of these factors to risk stratify BL patients was modest. In contrast, a low T1B IL-10/TNFα ratio at 3 months identified BL patients at high risk for progression to AR (ROC AUC 0.87) and poor 7-yr graft survival (52% vs. 92%, p=0.003), while BL patients with a high ratio had similar graft survival to patients with NI (91%, p=NS). Thus, progressive early allograft inflammation manifested as BL that progresses to late AR in the first post-transplant year represents a high-risk clinical state for poor allograft outcomes. Such high-risk status can be predicted by the T1B IL-10/TNFα ratio before irreversible scarring sets in, thus allowing timely risk stratification.
Keywords: B cells; acute rejection; cytokines; kidney biopsy; transplantation.
Copyright © 2022 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Comment in
-
A transitional B-cell cytokine biomarker for risk stratifying renal transplant patients with borderline rejection.Kidney Int. 2023 Apr;103(4):658-660. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.12.020. Kidney Int. 2023. PMID: 36948765 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
A Rejection Gene Expression Score in Indication and Surveillance Biopsies Is Associated with Graft Outcome.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 3;21(21):8237. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218237. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33153205 Free PMC article.
-
Transitional B cell cytokines predict renal allograft outcomes.Sci Transl Med. 2021 Feb 24;13(582):eabe4929. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abe4929. Sci Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33627487
-
Utility of Serial Protocol Biopsies Performed After 1 Year in Predicting Long-Term Kidney Allograft Function According to Histologic Phenotype.Exp Clin Transplant. 2018 Aug;16(4):391-400. doi: 10.6002/ect.2016.0323. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Exp Clin Transplant. 2018. PMID: 29206090
-
Risk factors associated with the deterioration of renal function: the role of protocol biopsies.Prilozi. 2007 Jul;28(1):291-302. Prilozi. 2007. PMID: 17932475 Review.
-
Chronic allograft nephropathy or interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy: what is in a name?Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2014 May;23(3):245-50. doi: 10.1097/01.mnh.0000444811.26884.2d. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2014. PMID: 24626060 Review.
Cited by
-
Distribution characteristics of circulating B cell subpopulations in patients with chronic kidney disease.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 27;13(1):20797. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47742-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38012211 Free PMC article.
-
A transitional B-cell cytokine biomarker for risk stratifying renal transplant patients with borderline rejection.Kidney Int. 2023 Apr;103(4):658-660. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.12.020. Kidney Int. 2023. PMID: 36948765 Free PMC article.
-
Limitations of biopsy-based transcript diagnostics to detect T-cell-mediated allograft rejection.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2025 Feb 4;40(2):294-307. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfae147. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2025. PMID: 38925651 Free PMC article.
-
The transformative potential of artificial intelligence in solid organ transplantation.Front Transplant. 2024 Mar 15;3:1361491. doi: 10.3389/frtra.2024.1361491. eCollection 2024. Front Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38993779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic establishment and maintenance of the human intestinal B cell population and repertoire following transplantation in a pediatric-dominated cohort.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 28;15:1375486. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1375486. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39007142 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

